(*Corresponding authors, #Authors with equal contributions)
115. Tan, Z.;# Hou, Y.;# Huang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Lu, P.; Zhang, X.* “Time-resolved genetically encoded indicators towards quantitative imaging of calcium dynamics in living cells”, ACS Sensors, accepted.
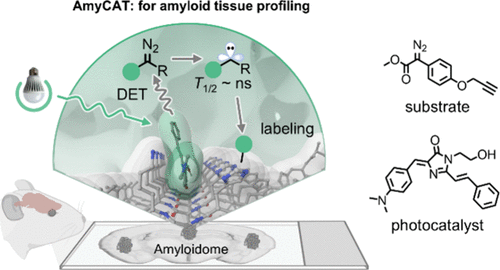
114. Feng, H.;# Guo, F.;# Wang, Y.;# You, M.; Xia, Q.; Wan, W.; Shen, D.; Shen, K.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.*; Liu, Y.* “Photo‐catalyzed labeling of amyloid deposits in human tissue to proteotype amyloidosis diseases”, Aggregate, accepted.
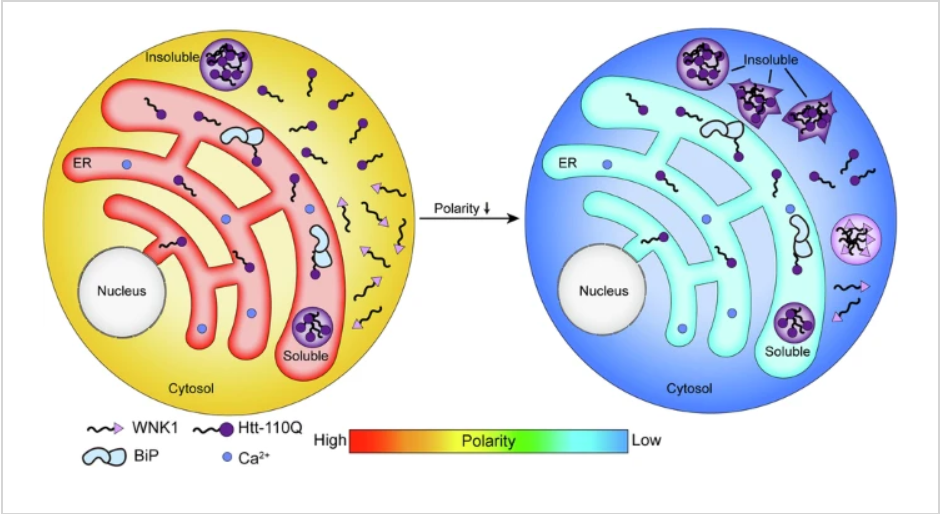
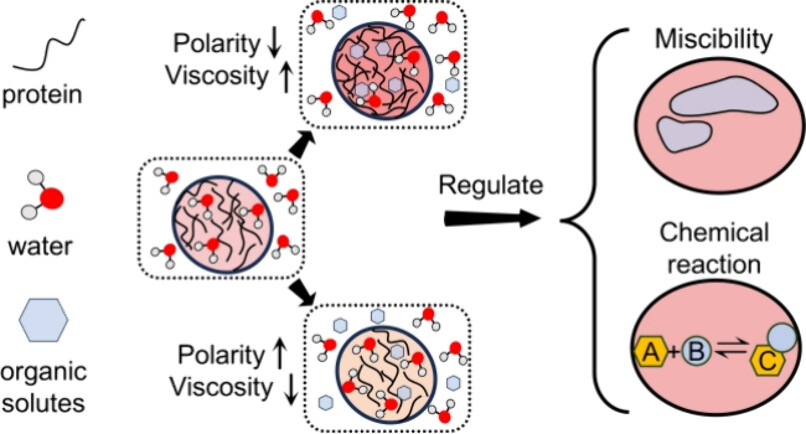
113. Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, P.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.* “The endoplasmic reticulum displays high polarity with low protein aggregation in human cells”, Commun. Biol. 2026, 9: 215.
112. Wang, Y.;#,* Zhu, J.;# Zhan, F.;# Guo, Y.; Xia, Y.; Liu, J.; Dai, P.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Luan, X.; Shen, X.; Cao, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Cao, L.;* Hou, S. X.* “PML targets and resolves structured protein inclusions to mitigate neurodegeneration”, Nat. Cell Biol. 2026, doi: 10.1038/s41556-026-01894-z.
111. Sun, R.; Deng, J.; Shen, D.; Yan, J.; Huang, Y.; Feng, H.; Li, M.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, X.;* Liu, Y.* “Dexter energy transfer photocatalytic microdissection of amyloid plaques in Alzheimer's disease”, JACS Au 2026, 6, 2: 1129-1140.
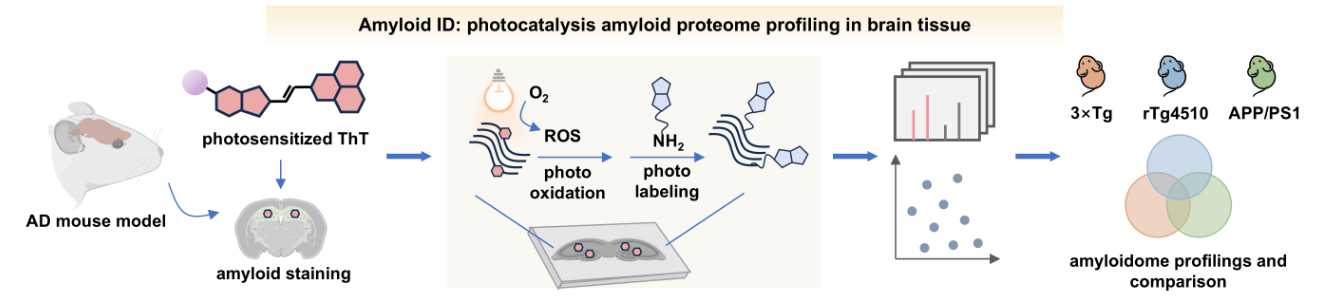
110. Feng, H.;# Zhao, Q.;# Guo, F.; Yan, J.; Zhao, N.; Ma, J.; Sun, R.; Shen, K.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.;* Liu, Y.* “Amyloid-ID: photocatalytic profiling of amyloid deposits in Alzheimer’s disease tissue”, Nat. Commun. 2026, 17: 1260.
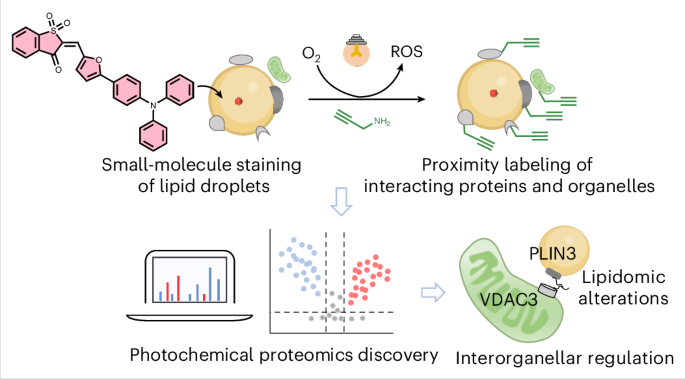
109. Guo, H.;# Wan, W.;# Huang, Y.;# Zhao, N.;# Wu, C.; Zhong, B.; Sun, R.; Feng, H.; Yan, J.; Shen, D.; Dong, X.; Zhao, Q.;* Zhang, X.;* Zhang, L.;* Liu, Y.* “LipoID profiles lipid droplet interactions and identifies interorganelle regulators”, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2026, doi: 10.1038/s41589-025-02127-4.
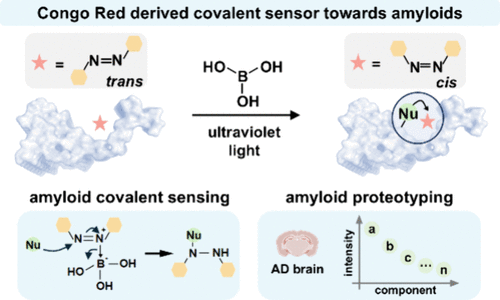
108. Feng, H.;#,* Gao, R.;# Guo, F.;# Wan, W.; Shen, D.; Yan, J.; Ge, Y.; Shen, K.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.* “Congo red derived covalent proteotyping sensor for amyloid deposits in Alzheimer’s disease”, ACS Sens. 2026, 11, 1: 27-33.
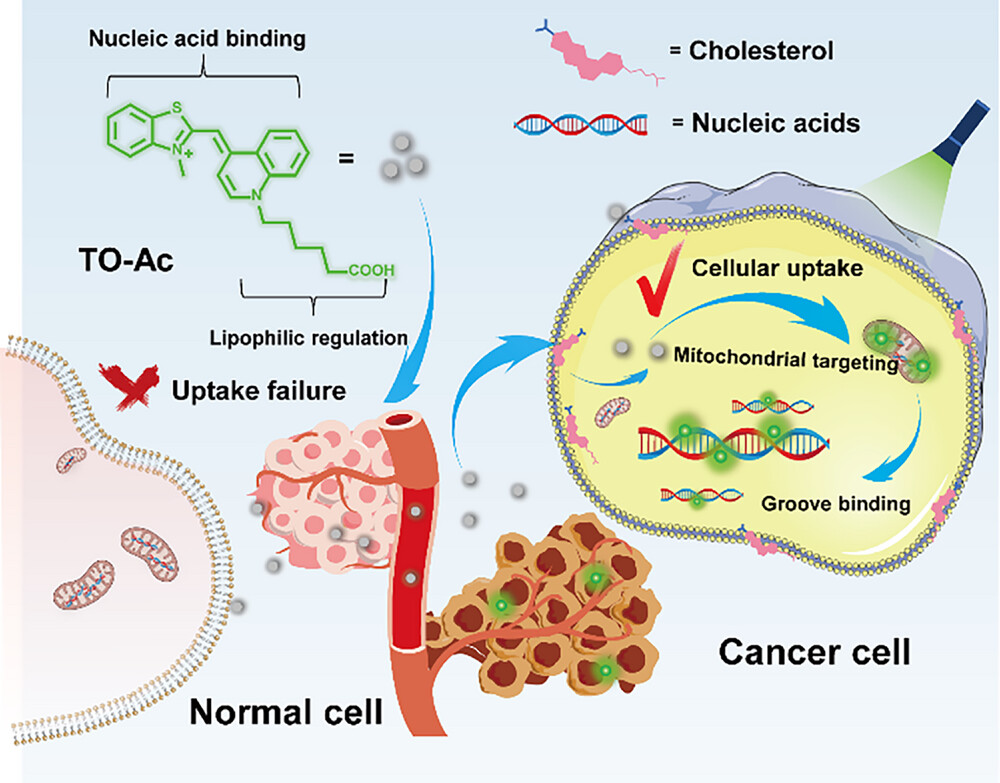
107. Xia, Z.; Xia, T.; Fei, J.; Du, J.; Zhang, X.;* Fan, J.;* Peng, X. “A probe design strategy based on cholesterol-induced differential cellular uptake for cancer cells specific penetration and imaging”, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2025, 64, 51: e202517406.
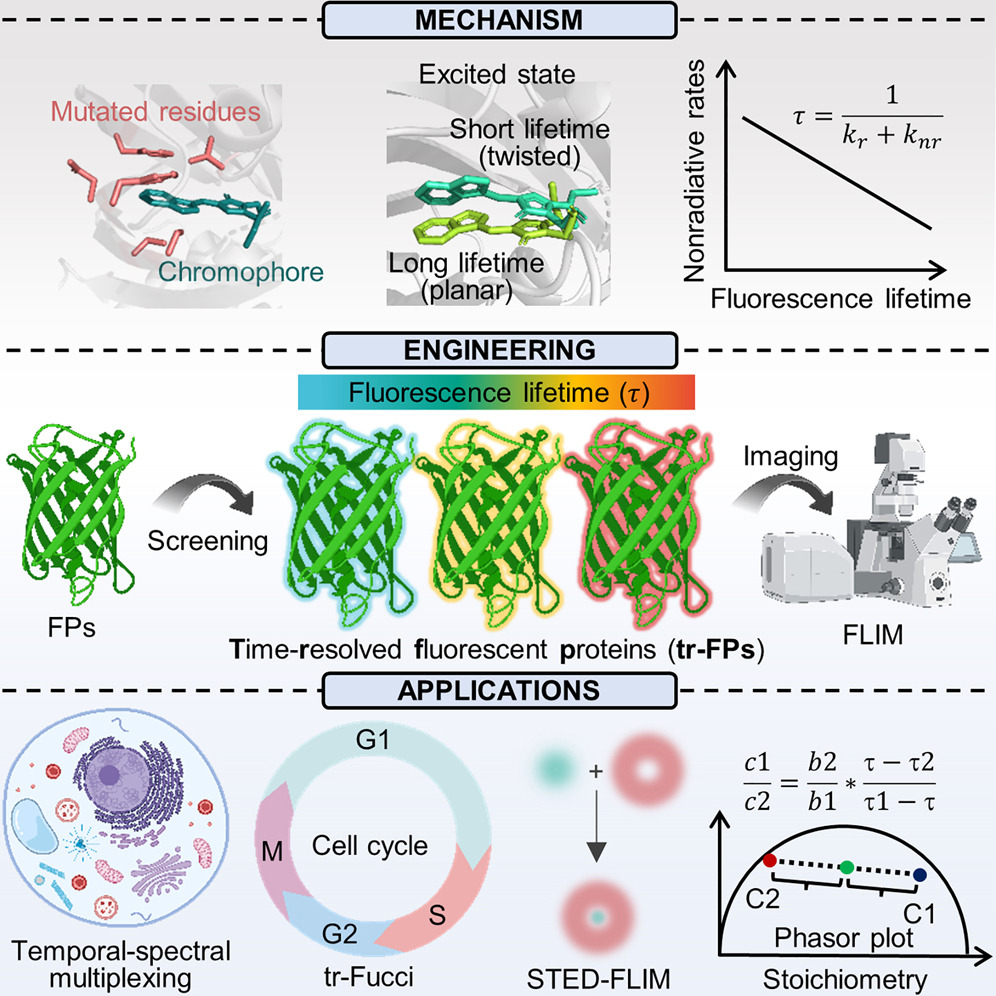
106. Tan, Z.;# Hsiung, C. -H.;# Feng, J.;# Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Chen, J.; Sun, K.; Lu, P.; Zang, J.; Yang, W.; Gao, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhu, T.; Lu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Zou, Y.; Liao, C.; Li, X.; Ye, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.* “Time-resolved fluorescent proteins expand fluorescent microscopy in temporal and spectral domains”, Cell 2025, 188: 6987-7005.
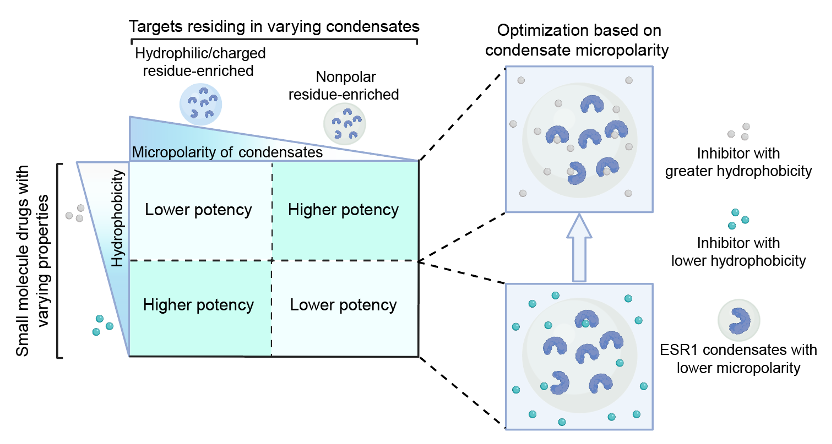
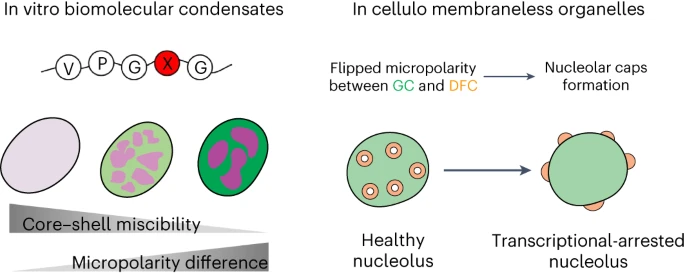
105. Ouyang, J.;# Chen, J.;# Wu, Z.; You, K.; Chen, T.; Gao, Y. Q.; Li, P.; Zhang, X.;* Li, T.* “Navigating condensate micropolarity to enhance small-molecule drug targeting”, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2025, doi: 10.1038/s41589-025-02017-9.
104. Pan, Y.; Lei, J.; Mou, S.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zeng, L.; Luo, F.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.* “Small molecules influence the physical microenvironment of biomolecular condensates”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 26: 22686-22696.
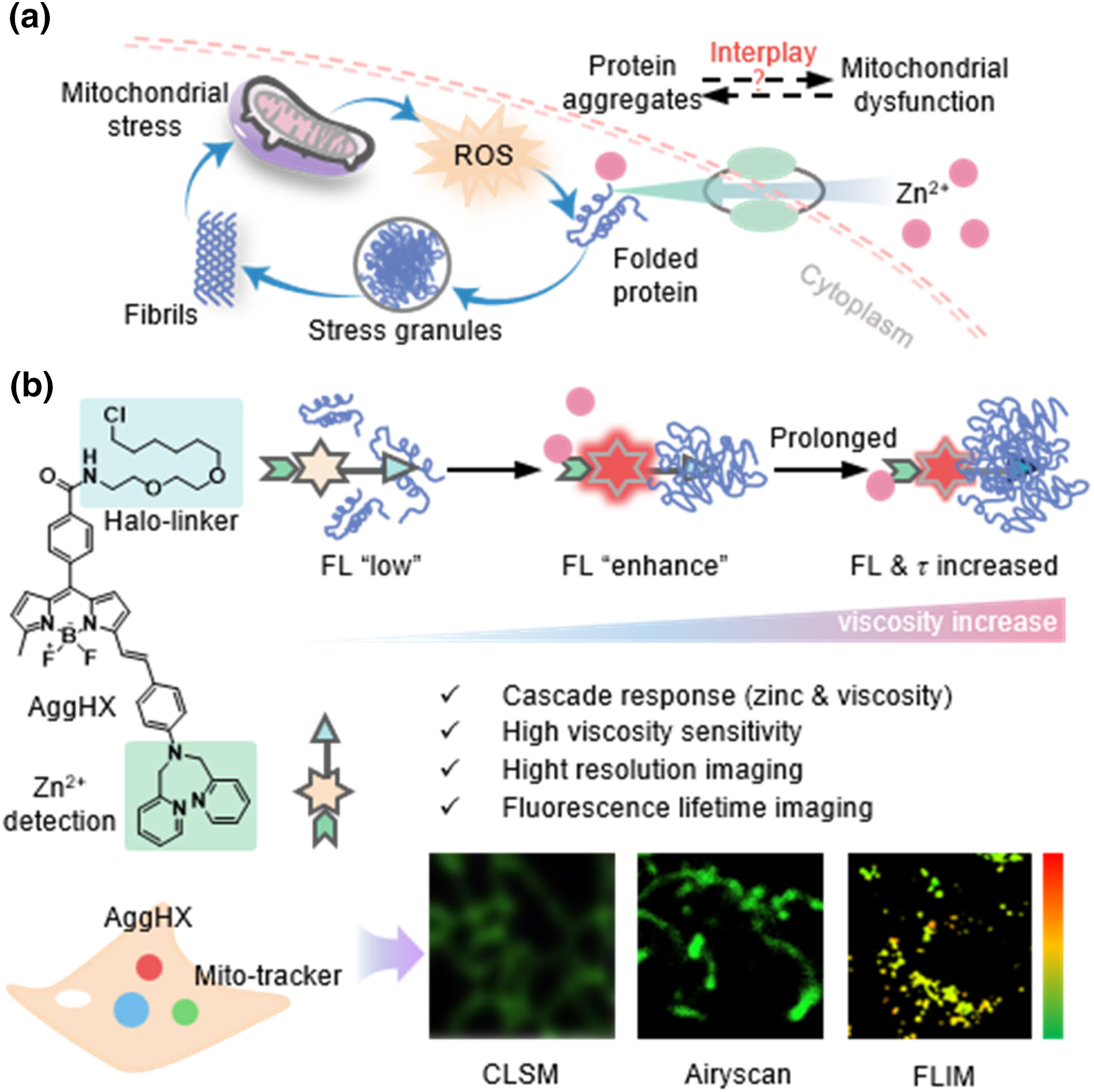
103. Zhai, J.;# Zhang, M.;# Chen, Z.;# Fang, J.; Ju, M.;* Shen, B.;* Zhang, X.* “Investigating the interplay between iron-mediated protein aggregation and mitochondrial damage using polarity-sensitive fluorescent lifetime probes”, Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 422: 138085.

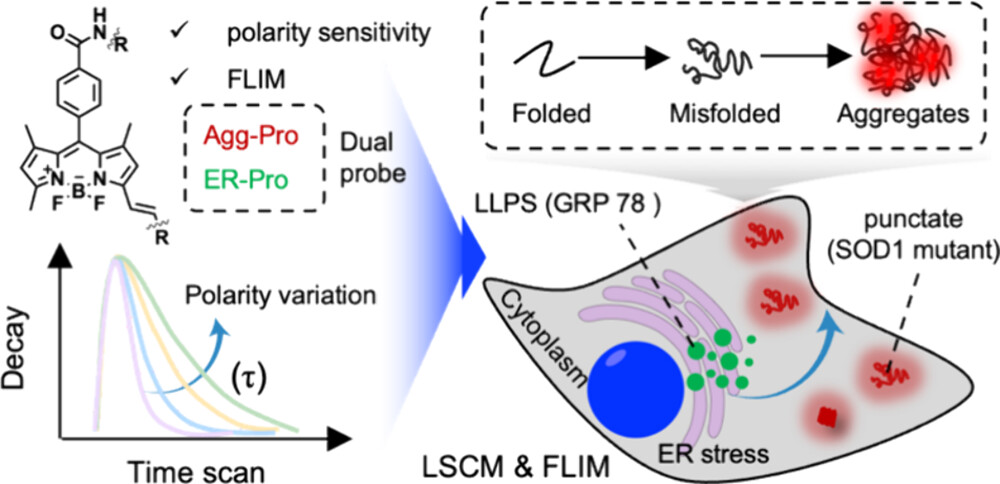
102. Li, J.;# Zi, X.;# Fang, J.; Liang, M.; Ju, M.;* Sun, Z.;* Shen, B.;* Zhang, X.* “Endoplasmic reticulum stress induces liquid-liquid phase separation of GRP78 and modulates protein aggregation dynamics”, ACS Sens. 2025, 10, 6: 4535-4543.
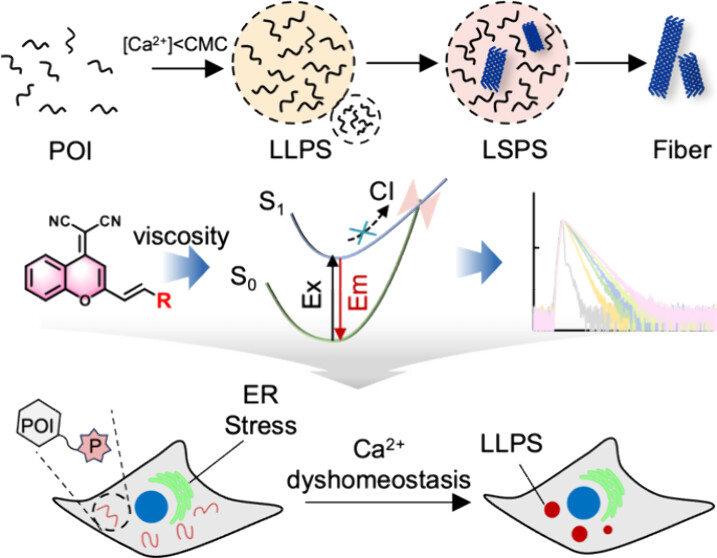
101. Wei, Y.;# Zi, X.;# Zhai, J.;# Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Sun, Z.; Ju, M.;* Zhang, X.;* Shen, B.* “Exploring endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction on protein phase separation using viscosity-sensitive fluorescent lifetime probe”, Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 18: 10038.
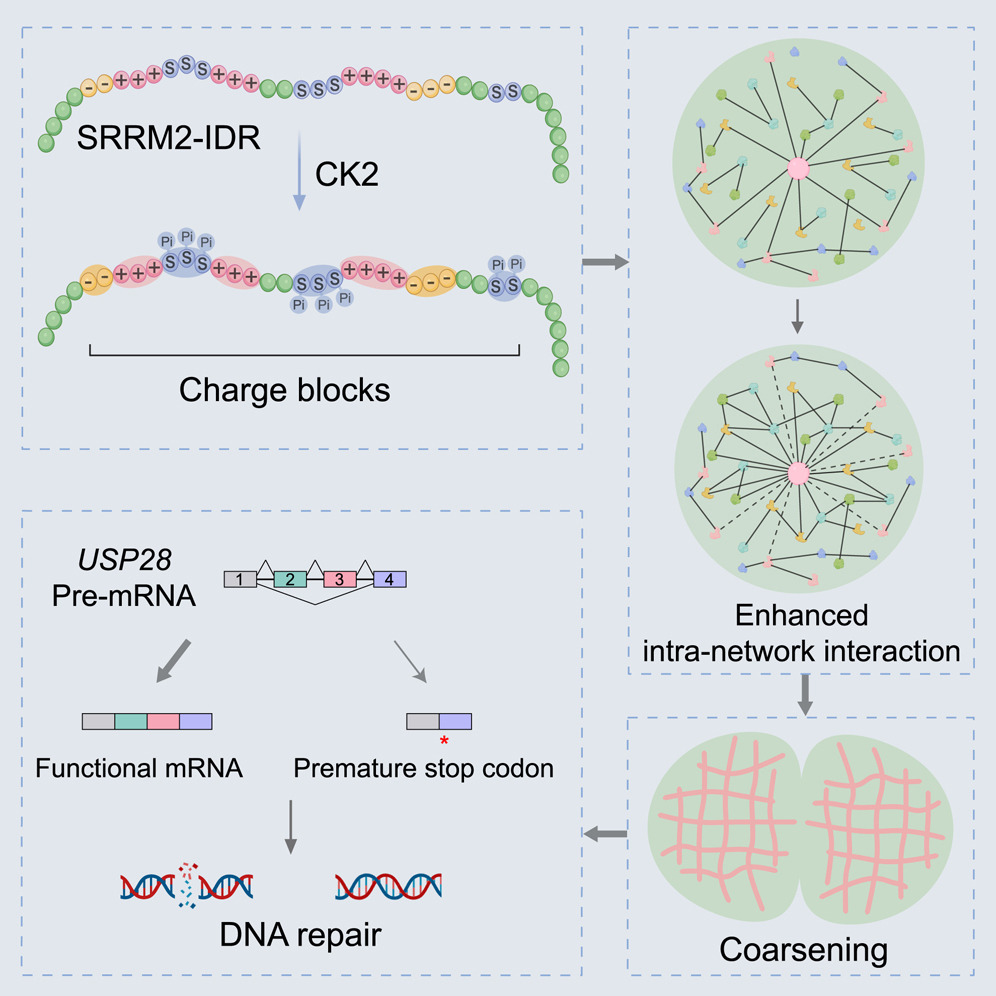
100. Zhang, M.;# Gu, Z.;# Sun, Y.;# Dong, Y.; Chen, J.; Shu, L.; Ma, S.; Guo, J.; Liang, Y.; Qu, Q.; Fang, N.; Zhong, C. -H.; Ge, Y.; Chen, Z.; Huang, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, B.* “Phosphorylation-dependent charge blocks regulate the relaxation of nuclear speckle networks”, Mol. Cell 2025, 85, 9: 1760.
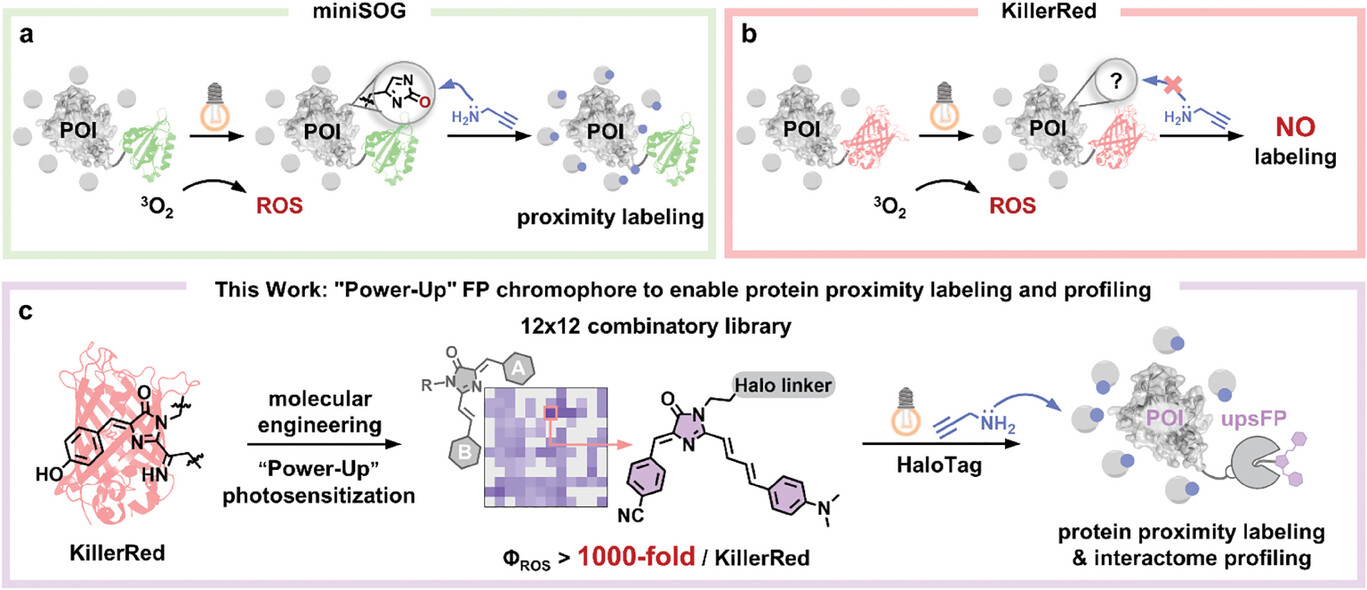
99. Sun, R.; Huang. Y.; Feng, H.; Zhao, N.; Wan, W.; Shen, D.; Zhong, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Q.;* Zhang, L.;* Liu, Y.* “1000 fold ultra-photosensitized fluorescent protein mimics towards photocatalytic proximity labeling and proteomic profiling functions”, Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 15: 2413063.
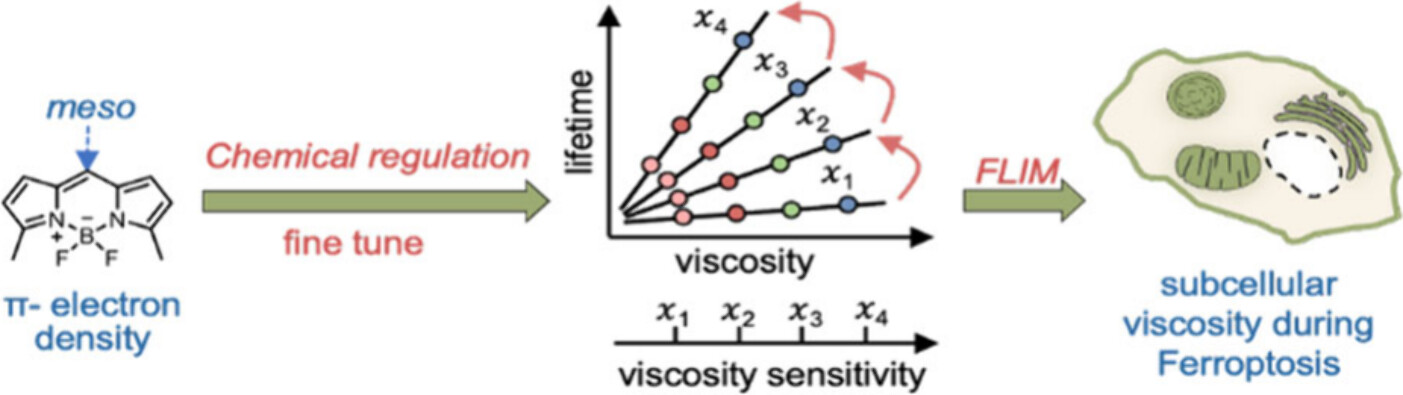
98. Dai, J.;# Hsiung, C. -H.;# Ding, L.;# Mou, S.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, B.;* Zou, Y.;* Fan, J.;* Zhang, X.* “Chemical control of fluorescence lifetime of molecular rotors provides insights into subcellular viscosities during ferroptosis”, Anal. Chem. 2025, 97, 18: 9893.
97. Zhou, L.;# Zhu, L.;# Wang, C.;# Xu, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.;* Zhang, X.;* Wang, H.* “Multiphasic condensates formed with mono-component of tetrapeptides via phase separation”, Nat. Commun. 2025, 16: 2706.

96. Wan, J.;# Huang, C.;# Chen, Z.;# Wan, J.;# Ding, W.; Liu, D.; Feng, L.; Meng, Y.; Li, M.; Ju, M.; Zhang, X.; Shen, B.;* Huang, H.* “Smart fluorogenic tools: From designing principles to visualization of multistep protein aggregation”, Coord. Chem. Rev. 2025, 535: 216625.

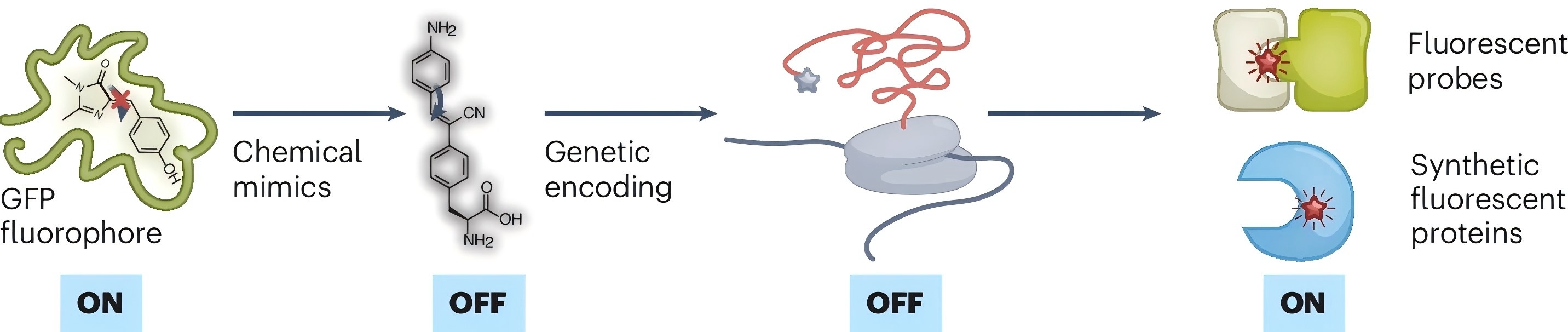
95. Hsiung, C. -H.; Zhang, X.* “Mimicking fluorophores from nature to generate artificial fluorescent proteins and biosensors”, Nat. Chem. 2024, 16: 1934-1935.
94. Hurtle, B.; Donnelly, C. J.; Zhang, X.; Thathiah, A.* “Live-cell visualization of tau aggregation in human neurons”, Commun. Biol. 2024, 7: 1143.
93. He, X.;# Li, J.;# He, W.;# Zhai, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, X.;* Shen, B.;* Huang, H.* “Exploring the interplay between zinc-induced protein dyshomeostasis and mitochondrial dysfunction using viscosity-sensitive sensor”, Smart Mol. 2024, 2: e20240047.
![]()
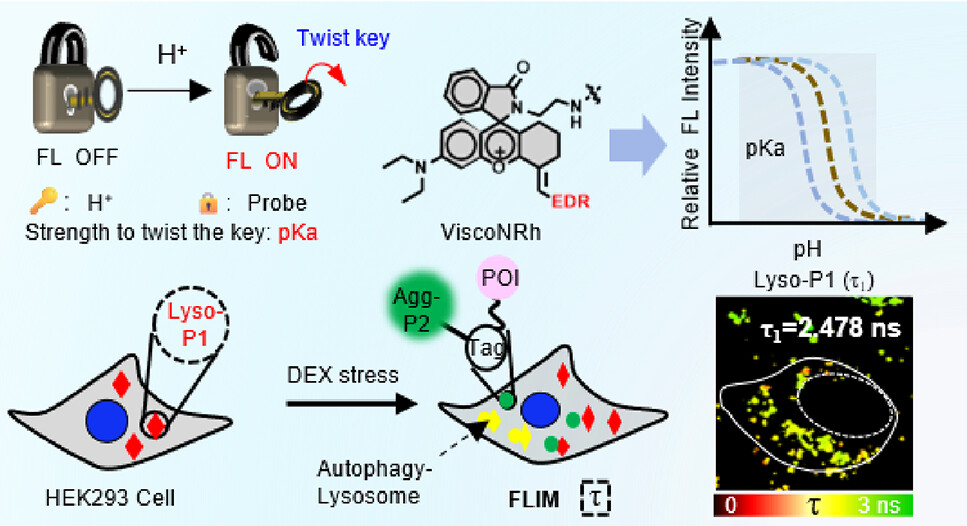
92. Wei, Y.;# Gao, X.;# Fang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.;* Zhang, X.;* Shen, B.* “Tailoring the pKa of fluorescence lifetime imaging probes to visualize aggrephagy and resolve its microenvironmental viscosity”, Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 35: 14160–14167.
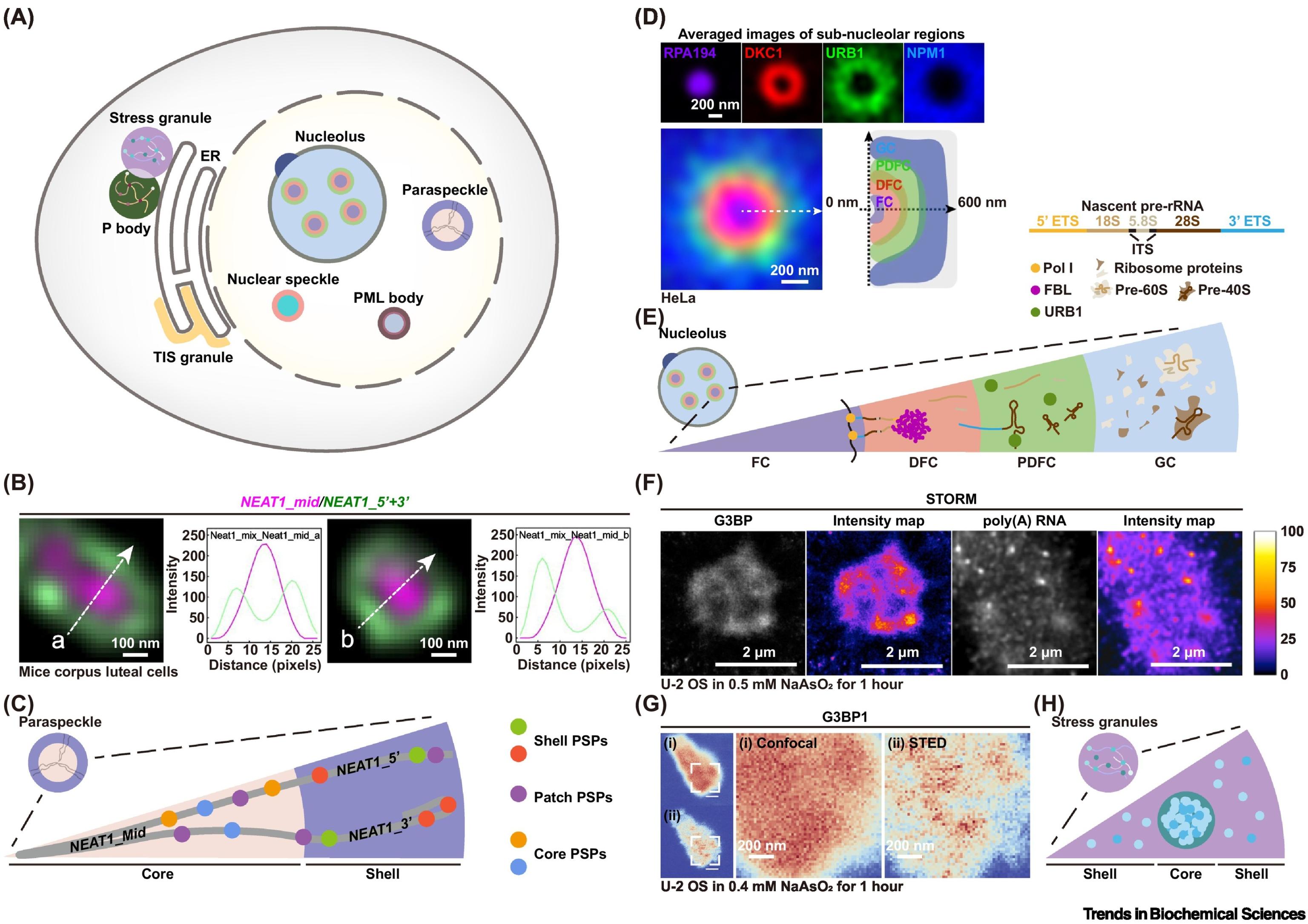
91. Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.* “Unveiling intracellular phase separation: advances in optical imaging of biomolecular condensates”, Trends Biochem. Sci. 2024, 49, 10: 901-915.
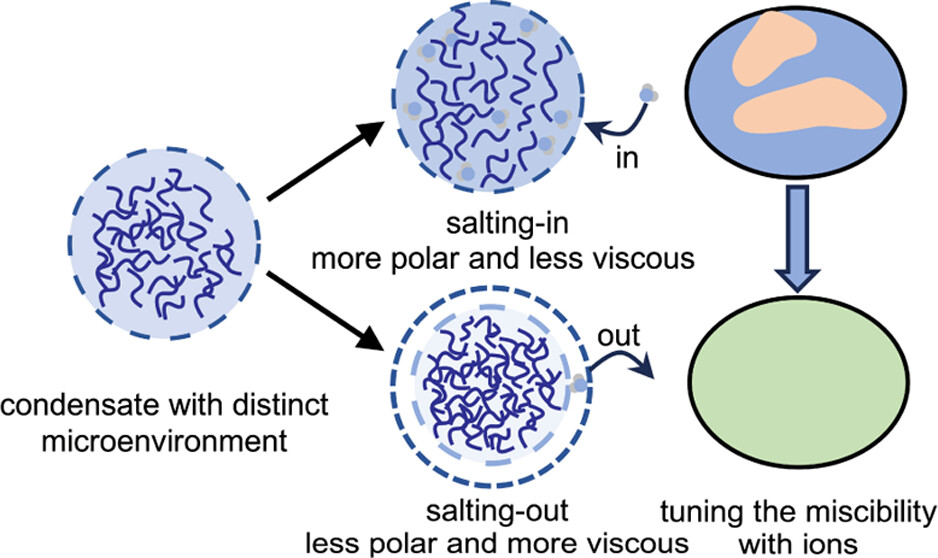
90. Zhu, L.; Pan, Y.; Hua, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.* “Ionic effect on the microenvironment of biomolecular condensates”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 20: 14307–14317.
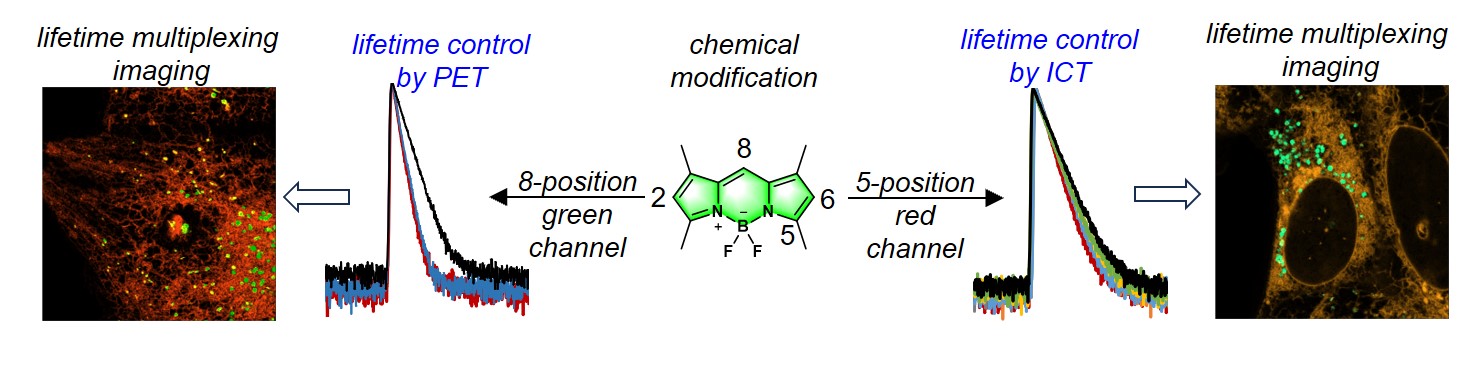
89. Ma, J.;# Luo, F.;# Hsiung, C. -H.; Dai, J.; Tan, Z.; Ye, S.; Ding, L.;* Shen, B.;* Zhang, X.* “Chemical control of fluorescence lifetime towards multiplexing imaging”, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, 25: e202403029.
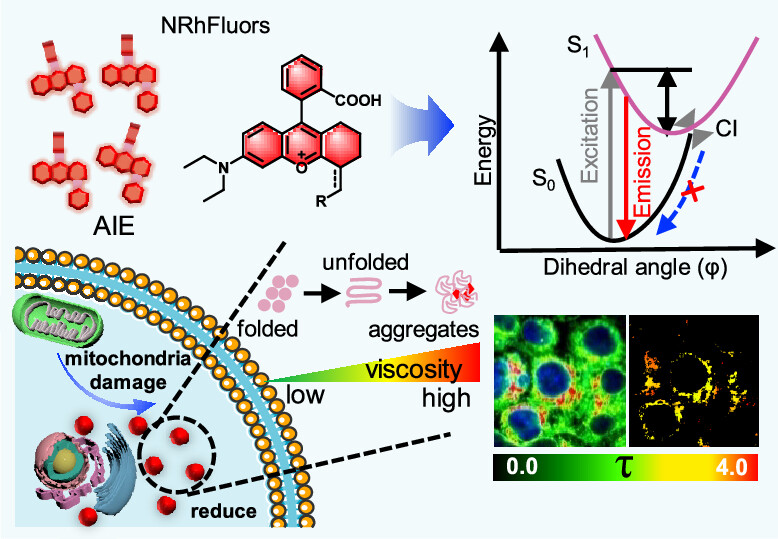
88. Huang, Y.;# Chang, M.;# Gao, X.; Fang, J.; Ding, W.; Liu, J.; Shen, B.;* Zhang, X.* “NRhFluors: Quantitative revealing the interaction between protein homeostasis and mitochondria dysfunction via fluo-rescence lifetime imaging”, ACS Central Sci. 2024, 10, 4: 842-851.
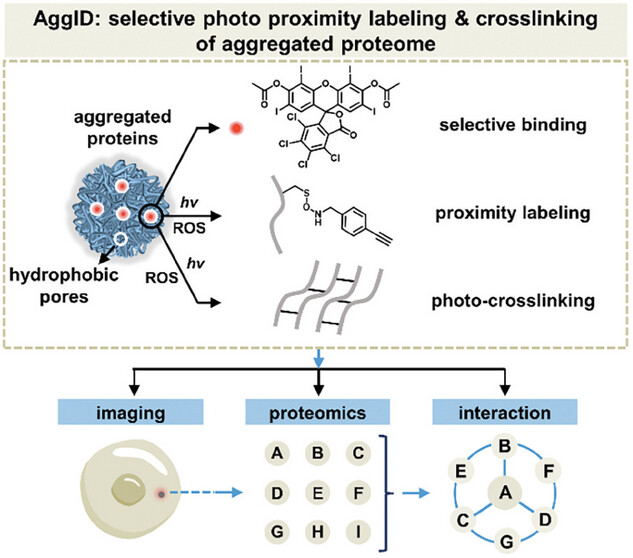
87. Feng, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, N.; Liang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.;* Liu, Y.* “A cell-permeable photosensitizer for selective proximity labeling and crosslinking of aggregated proteome”, Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 18: 2306950.
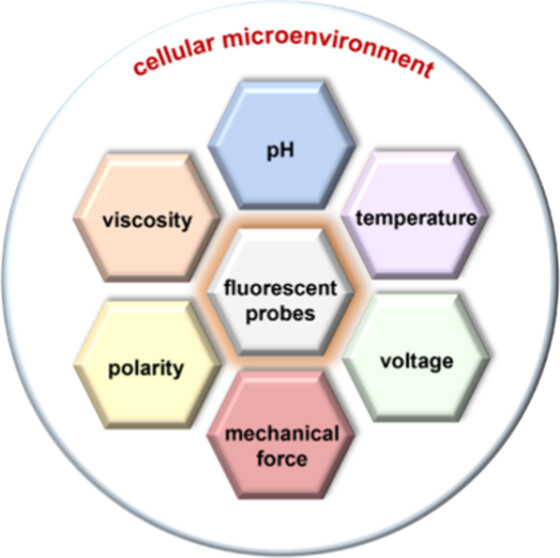
86. Ma, J.;# Sun, R.;# Xia, K.;# Xia, Q.;# Liu, Y.;* Zhang, X.* “Design and application of fluorescent probes to detect cellular physical microenvironments”, Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 4: 1738-1861.
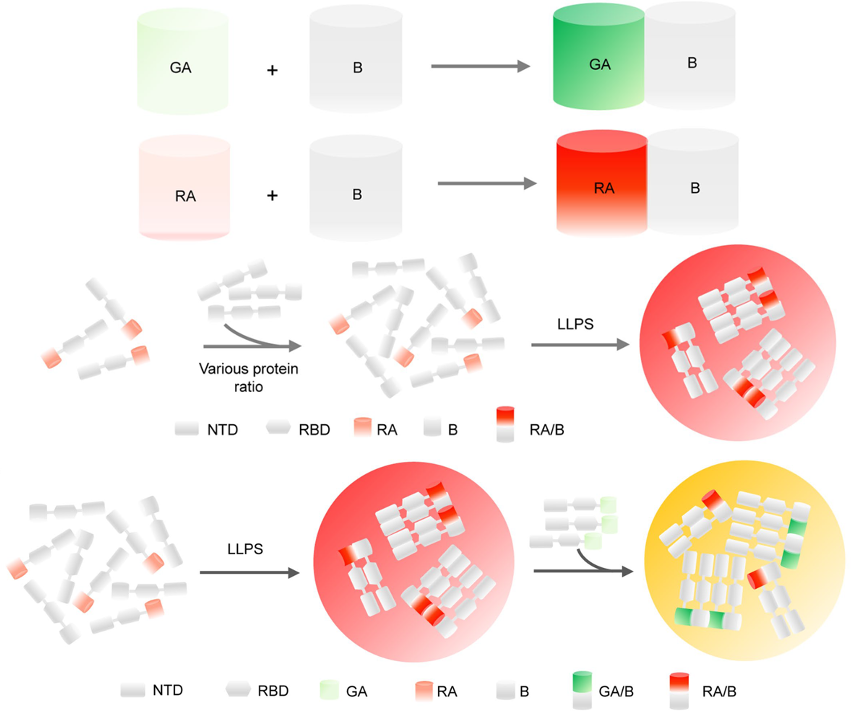
85. Huang, Y.; Chen, J.; Hsiung, C. -H.; Bai, Y.; Tan, Z.; Ye, S.; Zhang, X.* “Detecting protein-protein interaction during liquid-liquid phase separation using fluorogenic protein sensors”, Mol. Biol. Cell 2024, 35, 3: ar41.
84. Hoelzel, C.;# Bai, Y.;# Wang, M.; Liu, Y.;* Zhang, X.* “High-fidelity assay based on turn-off fluorescence to detect the perturbations of cellular proteostasis”, ACS Bio. & Med. Chem. Au. 2024, 4, 2: 111–118.

83. Zhang, X.;* Booker, S.* “Seeing is believing: advances in biological imaging”, ACS Bio. & Med. Chem. Au. 2024, 4: 1-3.
82. Wang, J.; Ma, X.; Hu, Y.; Feng, G.; Guo, C.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H.* “Regulation of micro- and small-exon retention and other splicing processes by GRP20 for flower development”, Nat. Plants 2024, 10: 66-85.
81. Ye, S.; Latham, A. P.; Tang, Y.; Hsiung, C. -H.; Chen, J.; Luo, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, X.* “Micropolarity governs the structural organization of biomolecular condensates”, Nat. Chem. Biol. 2024, 20: 443–451.
![]()
80. Latham, A. P.; Zhu, L.; Sharon, D. A.; Ye, S.; Willard, A. P.; Zhang, X.;* Zhang, B.* “Microphase separation produces interfacial environment within diblock biomolecular condensates”, eLife 2024, https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.90750.3.
79. Dai, J.; Zhang, X.* “Chemical regulation of fluorescence lifetime”, Chem. Biomed. Imaging 2023, 1, 9: 796–816.
78. Bai, Y.;# Zhang, S.;# Dong, H.;# Liu, Y.; Liu, C.;* Zhang, X.* “Advanced techniques for detecting protein misfolding and aggregation in cellular environments”, Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 21: 12254-12311.
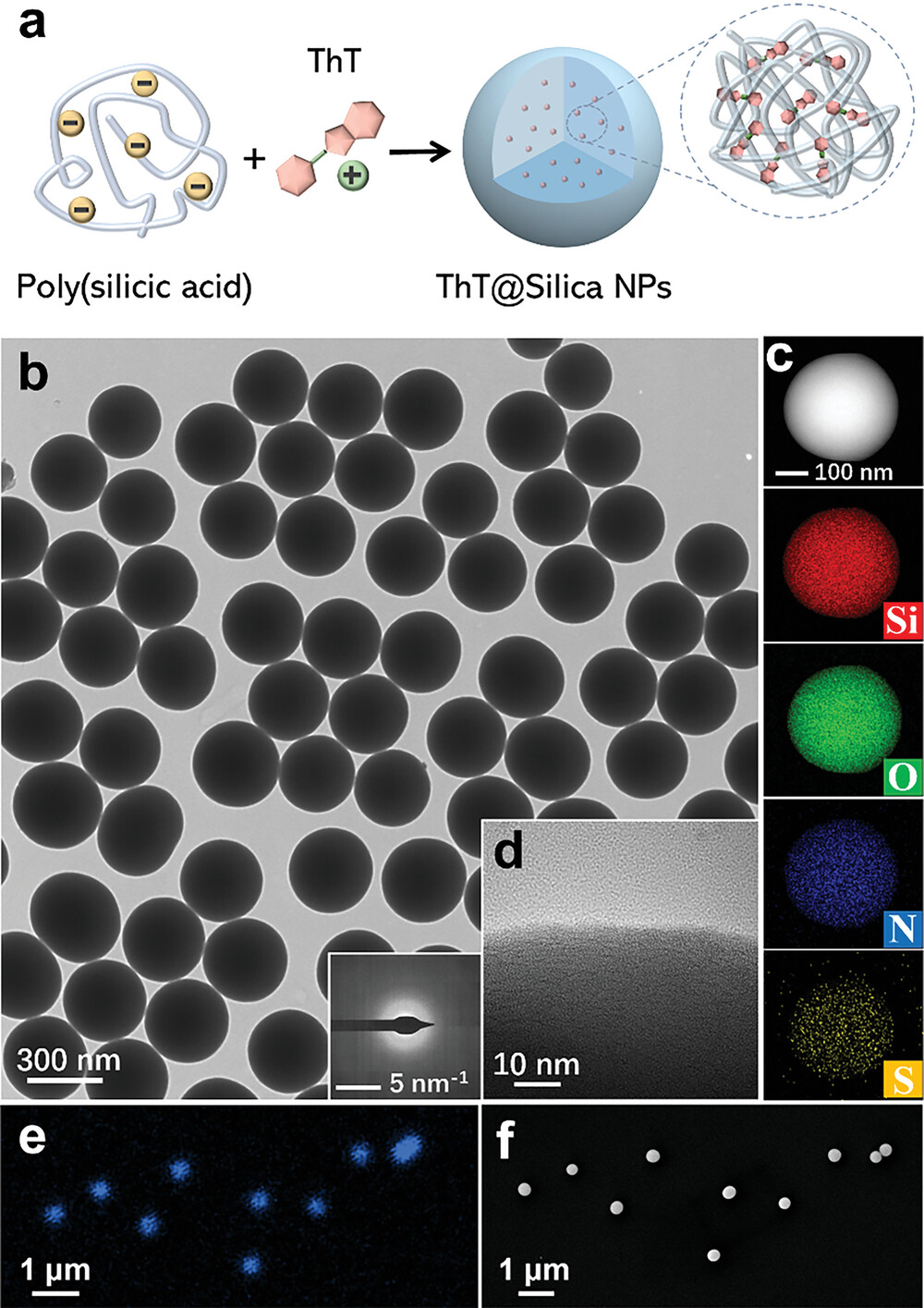
77. Cheng, X.; Pu, Y.; Ye, S.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.* “Measuring solvent exchange in silica nanoparticles with rotor-based fluorophore”, Adv. Mater. 2023, 36: 2305779.
76. Zhang, X.* and Tang, B. Z.* et al., “Aggregation-induced emission (AIE), life and health”, ACS Nano 2023, 17, 15: 14347–14405.
75. Liu, C.;* Zhang, X.* “Navigating the terrain of protein aggregation and phase separation - A chemical biology perspective”, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2023, 77: 102386.
74. Ma, Q.; Wang, M.; Huang, Y.; Nie, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, D. D.; Wang, Z.; Ding, S.; Qian, N.; Liu, Y.;* Pan, X.* “Identification of a novel transthyretin mutation D39Y in a cardiac amyloidosis patient and its biochemical characterizations”, Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10: 1091183.
73. Jung, K. H.; Sun, J.; Hsiung, C. -H.; Lian, X. L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.* “Nuclear bodies protect phase separated proteins from degradation in stressed proteome”, eLife 2023, https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.88237.1.
72. Shen, B.; Liu, L.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J.; Feng, H.; Liu, Y.;* Huang, H.;* Zhang, X.* “Installing hydrogen bonds as a general strategy to control viscosity sensitivity of molecular rotor fluorophores”, Aggregate 2024, 5, 1: e421.
71. Shen, D.;# Zhao, Q.;# Wang, M.; Zhong, B.; Jin, W.; Huang, Y.; Jin, H.; Jing, B.; Wan, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.;* Liu, Y.* “Developing an affinity-based chemical proteomics method to in-situ capture amorphous aggregated proteome and profile its heterogeneity in stressed cells”, Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 15: 6358–6366.
70. Zhang, Z.;# Zhu, L.;# Feng, J.;# Zhang, H.;* Zhang, X.;* Sun, J. Z.;* Tang, B. Z.* “In situ monitoring of protein aggregation via clusteroluminescence”, Mater. Chem. Front. 2023, 7: 713-719.
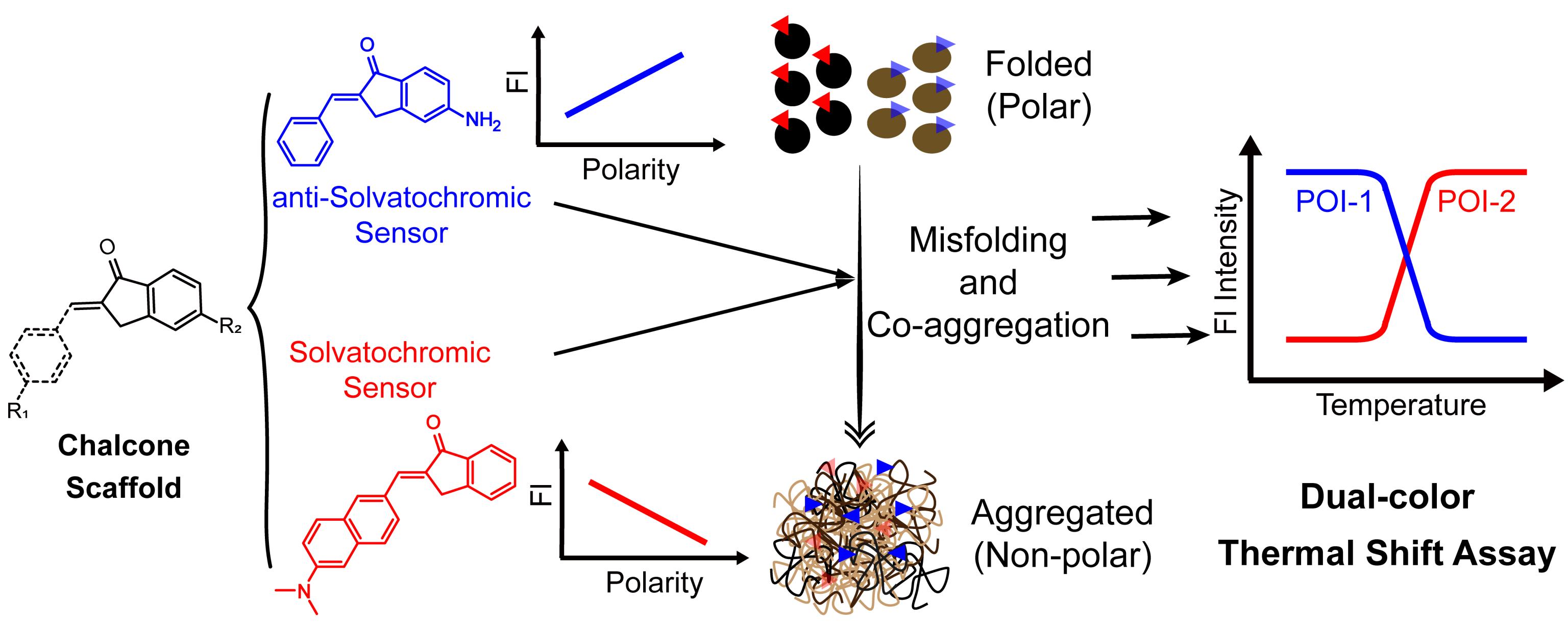
69. Bai, Y.; Wan, W.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, L.; Jing, B.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.;* Liu, Y.* “Tailoring the positive and negative solvatochromism for chalcone analogues to detect heterozygous protein co-aggregation”, Chem. Comm. 2023, 59: 4016–4019.
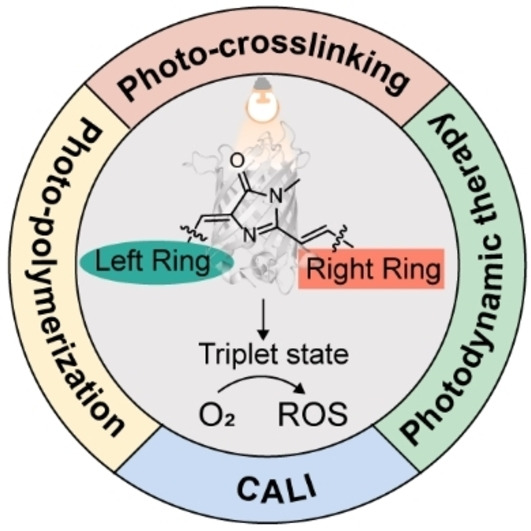
68. Feng, H.;# Zhao, Q.;# Zhang, B.; Hu, H.; Liu, M.; Wu, K.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.;* Zhang, L.;* Liu, Y.* “Enabling photo-crosslinking and photo-sensitizing properties for synthetic fluorescent protein chromophores”, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, 2: e202215215.
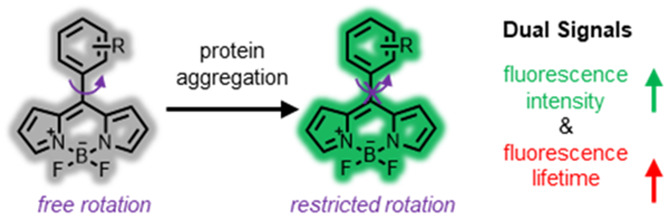
67. Shen, B.;# Jung, K. H.;# Ye, S.; Hoelzel, C. A.; Wolstenholme, C. H.; Huang, H.;* Liu, Y.;* Zhang, X.* “A dual-functional BODIPY-based molecular rotor probe reveals different viscosity of protein aggregates in live cells”, Aggregate 2023, 4, 3: e301.
66. Liu, L.;# Huang, Y.;# Zhou, Y.;# Zhao, Y.; Qi, J.; Zhang, X.;* Shen, B.* “Fluorogenic toolbox for visualizing protein aggregation: From designing principles to biological application”, TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 157: 116764.
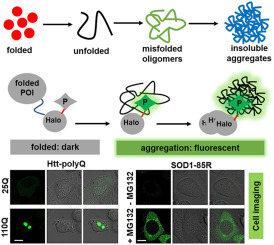
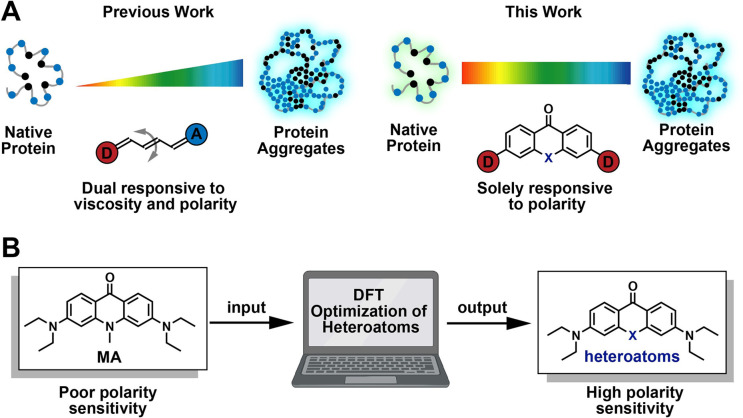
65. Wang, L.; Hsiung, C. -H.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Loredo, A.; Zhang, X.;* Xiao, H.* “Xanthone-based solvatochromic fluorophores for quantifying micropolarity of protein aggregates”, Chem. Sci. 2022,13, 42: 12540-12549.
64. Melo, E. P.;* Konno, T.; Farace, I.; Awadelkareem, M. A.; Skov, L. R.; Teodoro, F.; Sancho, T. P.; Paton, A. W.; Paton, J. C.; Fares, M.; Paulo, P. M. R.; Zhang, X.; Avezov, E.* “Stress-induced protein disaggregation in the endoplasmic reticulum catalysed by BiP”, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13: 2501.
63. Ye, S.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, X.* “Principles, modulation, and applications of fluorescent protein chromophores”, Chem. Phys. Rev. 2022, 3, 1: 011308.
62. Ye, S.;# Hsiung, C. -H.;# Tang, Y.; Zhang, X.* “Visualize the multi-step process of protein aggregation in live cells”, Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 3: 381–390.
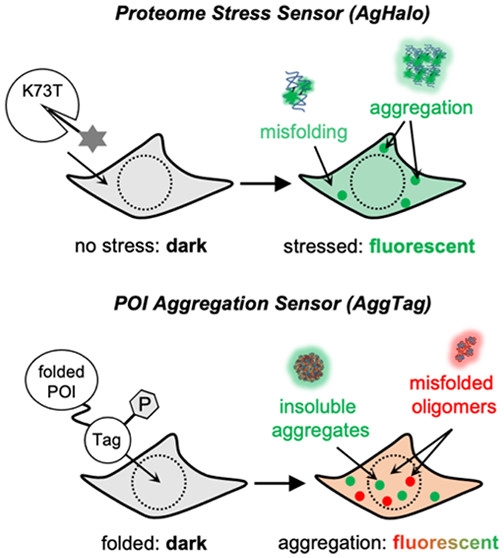
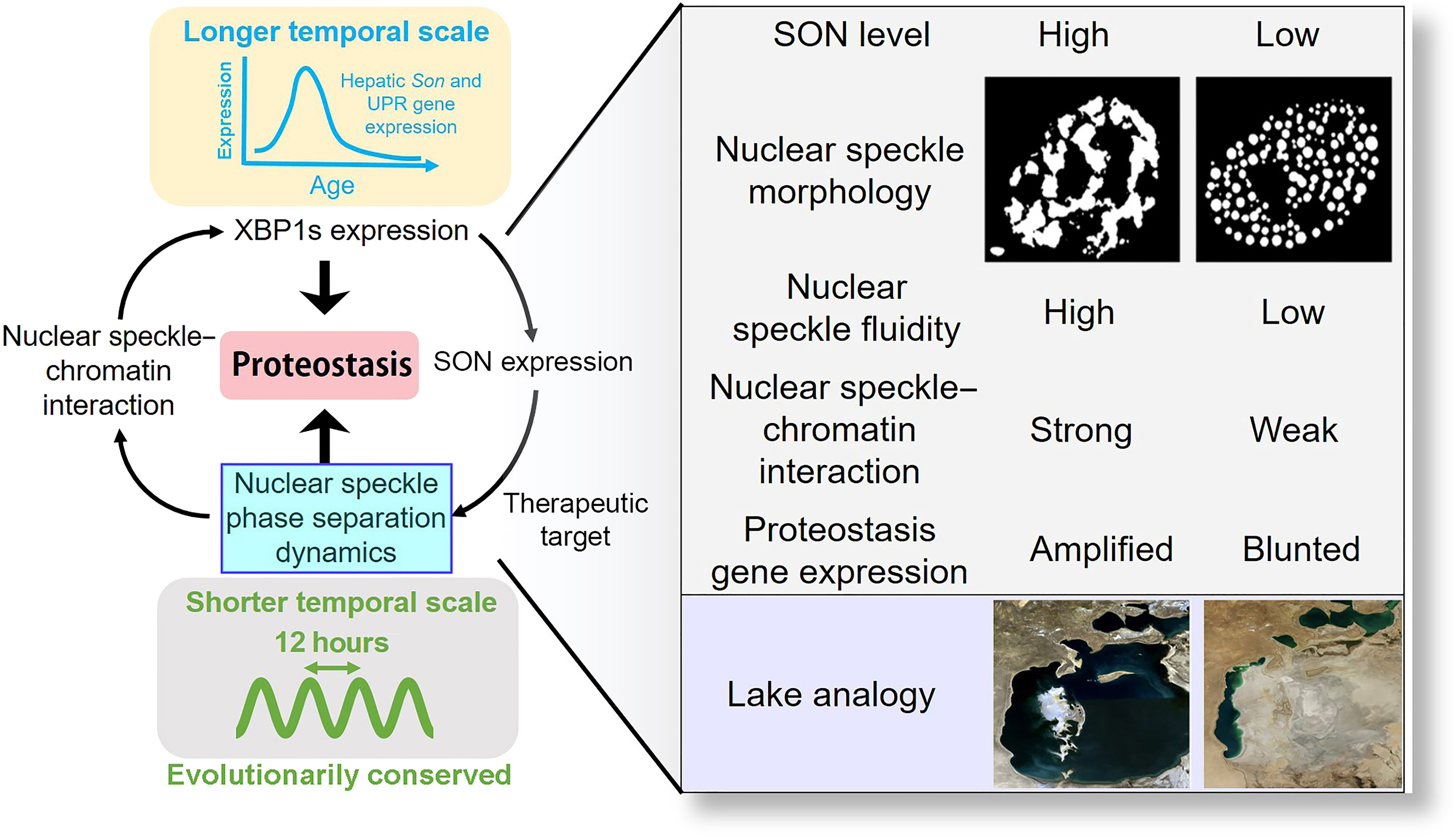
61. Dion, W.;# Ballance, H.;# Lee, J.; Pan, Y.; Irfan, S.; Edwards, C.; Sun, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Zhu, B.* “Four-dimensional nuclear speckle phase separation dynamics regulate proteostasis", Sci. Adv. 2022, 8: eabl4150.
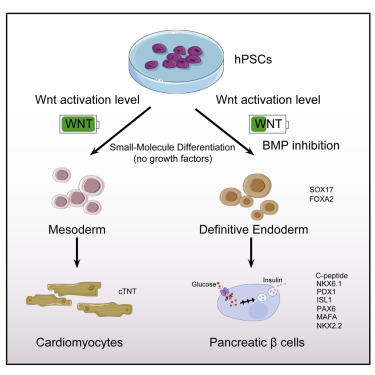
60. Jiang, Y.; Chen, C.; Randolph, L. N.; Ye, S.; Zhang, X.; Bao, X.; Lian, X. L.* “Generation of pancreatic progenitors from human pluripotent stem cells by small molecules”, Stem Cell Rep. 2021, 16, 9: 2395-2409.
59. Tang, S.;# Wang, W.;# Zhang, X.* “Direct visualization and profiling of protein misfolding and aggregation in live cells”, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2021, 64: 116-123.
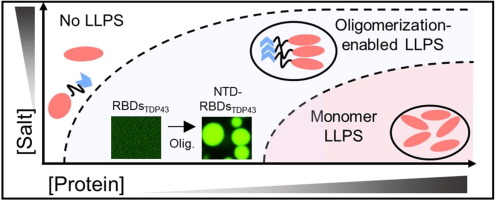
58. Carter, G. C.; Hsiung, C. -H.; Simpson, L.; Yang, H.; Zhang, X.* “N-terminal domain of TDP43 enhances liquid-liquid phase separation of globular proteins”, J. Mol. Biol. 2021, 433, 10: 166948.
57. Tang, S.;# Ye, S.;# Zhang, X.* “When aggregation-induced emission meets protein aggregates”, Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, 6: nwab013.
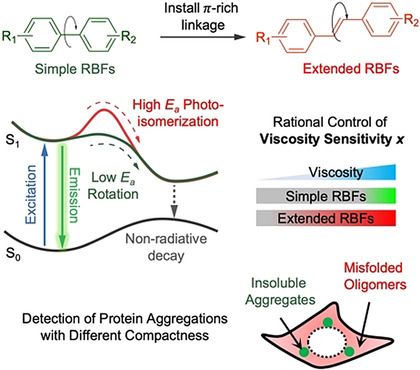
56. Ye, S.; Zhang, H.; Fei, J.; Wolstenholme, C. H.; Zhang, X.* “A general strategy to control viscosity sensitivity of molecular rotor-based fluorophores”, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 3: 1339-1346.
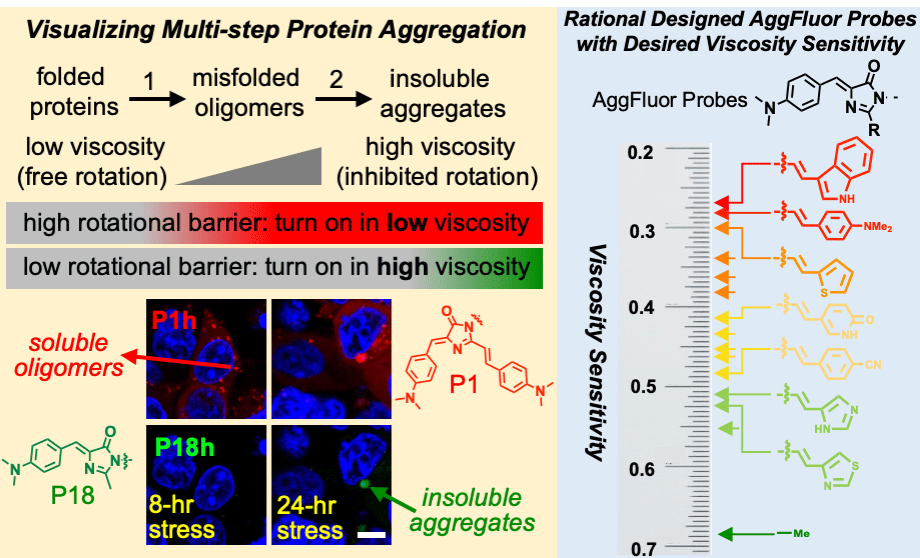
55. Wolstenholme, C. H.; Hu, H.; Ye, S.; Funk, B. E.; Jain, D.; Hsiung, C.-H.; Ning, G.; Liu, Y.;* Li, X.;* Zhang, X.* “AggFluor: Fluorogenic toolbox enables direct visualization of the multi-step protein aggregation process in live cells”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 41: 17515–17523. (highlighted by JACS Spotlights, Protein Aggregation: It’s a Process).
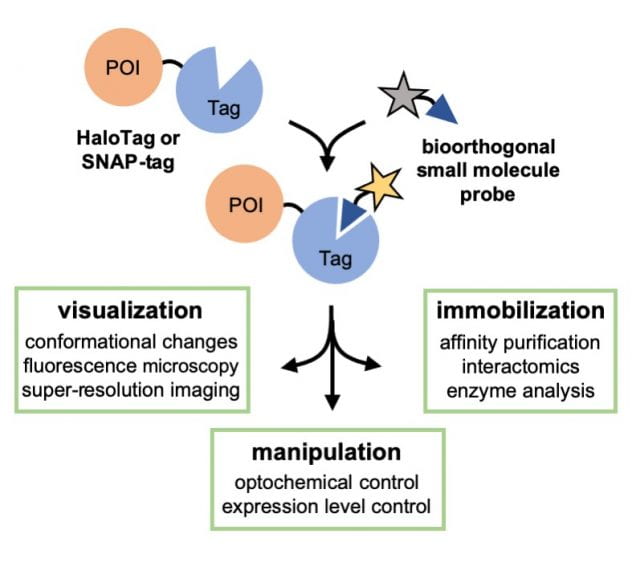
54. Hoelzel, C. A.; Zhang, X.* “Visualizing and manipulating biological processes by using HaloTag and SNAP-Tag technologies”, ChemBioChem 2020, 21, 14: 1935-1946.
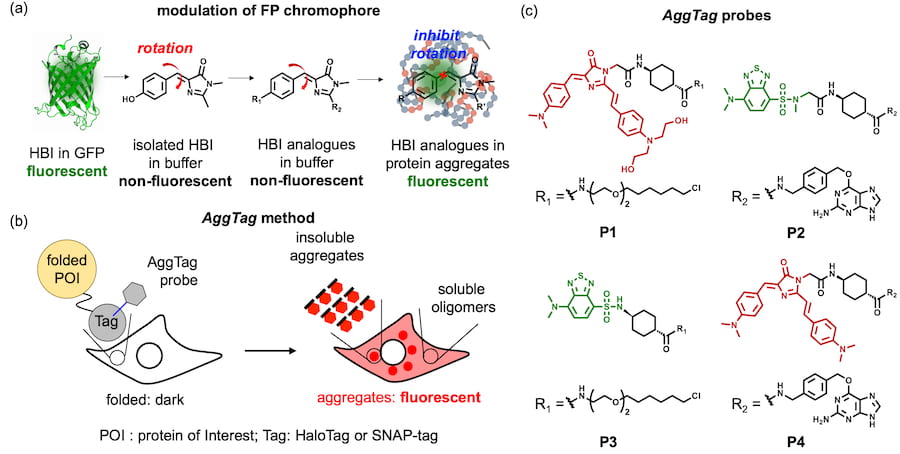
53. Jung, K. H.; Zhang, X.* “Fluorogenic detection of protein aggregates in live cells using the AggTag method”, Methods Enzymol. 2020, 639: 1-22.
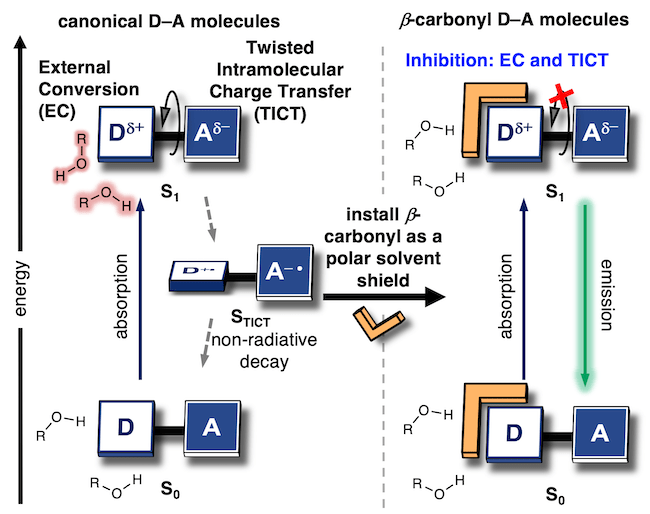
52. Hoelzel, C. A.; Hu, H.; Wolstenholme, C. H.; Karim, B. A.; Munson, K. T.; Jung, K. H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yennawar, H. P.; Asbury, J. B.; Li, X.;* Zhang, X.* “A general strategy to enhance donor-acceptor molecules using solvent-excluding substituents”, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 12: 4785-4792.
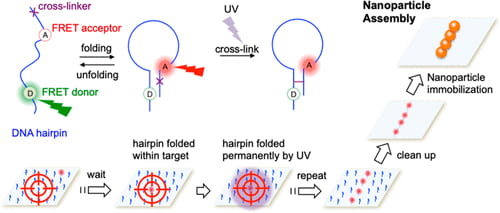
51. Kim, S. H.; Liu, Y.; Hoelzel, C.; Zhang, X.;* Lee, T. -H.* “Super-resolution optical lithography with DNA”, Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 9: 6035-6042.
50. Jung, K. H.; Kim, S. F.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.* “A fluorogenic AggTag method based on Halo- and SNAP-tags to simultaneously detect aggregation of two proteins in live cells”, ChemBioChem 2019, 20, 8: 1078-1087.

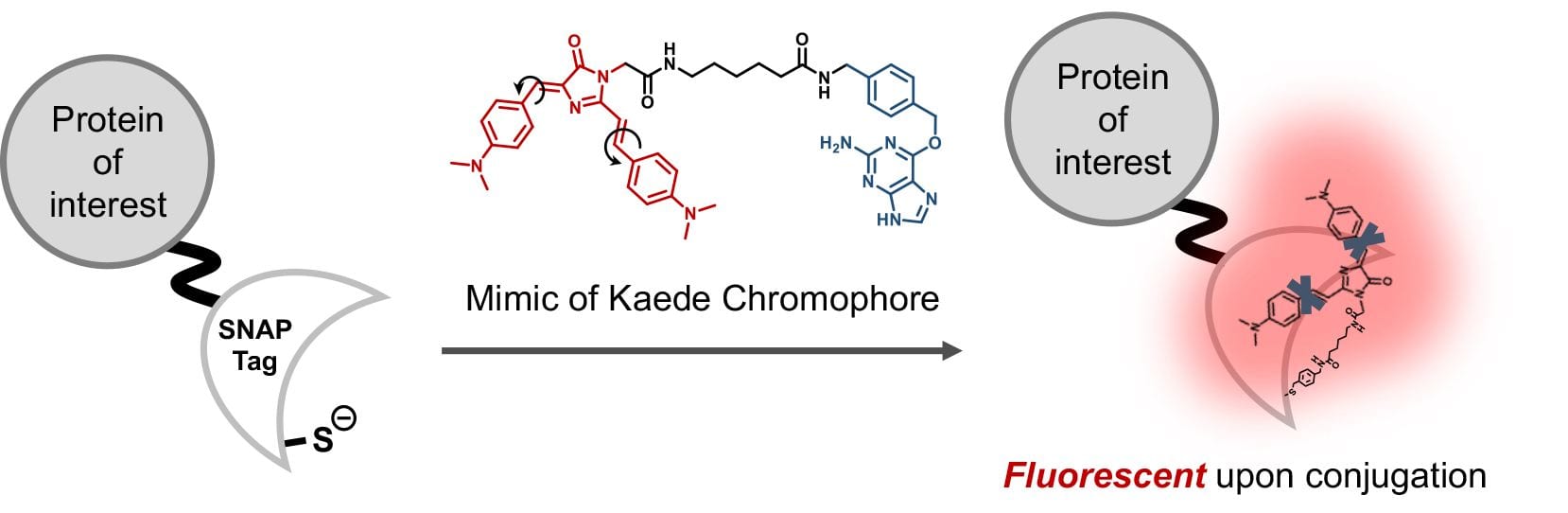
49. Jung, K. H.; Fares, M.; Grainger, L. S.; Wolstenholme, C. H.; Hou, A.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.* “A SNAP-tag fluorogenic probe mimicking the chromophore of the red fluorescent protein Kaede”, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 7: 1906-1915.
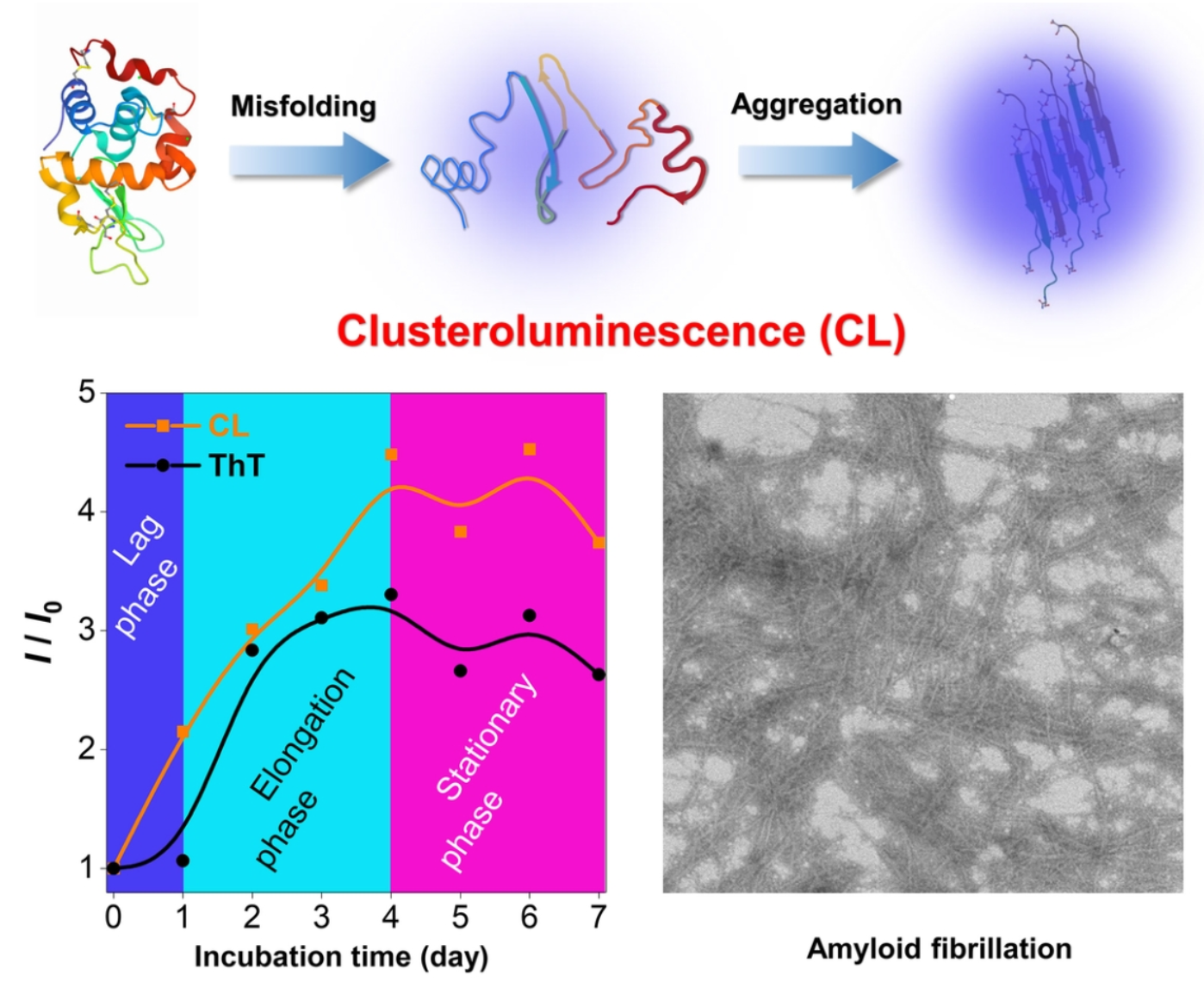
48. Liu, Y.; Fares, M.; Zhang, X.* “Monitoring proteome stress in live cells using HaloTag-based fluorogenic sensor”, Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1873: 171-182.
47. Fares, M.; Zhang, X.* “Quantification of cellular proteostasis in live cells by fluorogenic assay using the AgHalo sensor”, Curr. Protoc. Chem. Biol. 2018, 11, 1: e58.
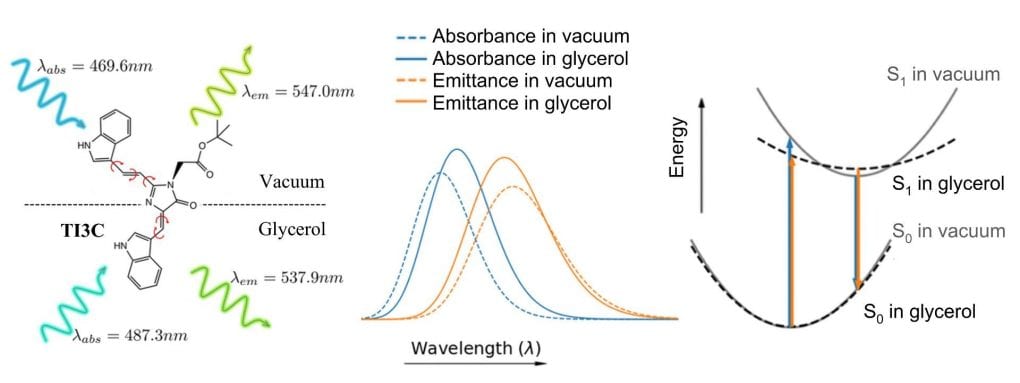
46. Hu, H.; Wolstenholme, C. H.; Zhang, X.;* Li, X.* “Inverted solvatochromic stokes shift in GFP-like chromophores with extended conjugation”, Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 31, 4: 599-607.
45. Liu, Y.; Miao, K.; Li, Y.; Fares, M.; Chen, S.; Zhang, X.* “A HaloTag-based multicolor fluorogenic sensor visualizes and quantifies proteome stress in live cells using solvatochromic and molecular rotor-based fluorophores”, Biochemistry 2018, 57, 31: 4663-4674.
44. Leach, B. I.; Zhang, X.; Kelly, J. W.; Dyson, H. J.; Wright, P. E.* “NMR measurements reveal the structural basis of transthyretin destabilization by pathogenic mutations”, Biochemistry 2018, 57, 30: 4421-4430.

43. Liu, Y.; Wolstenholme, C. H.; Carter, G. C.; Liu, H.; Hu, H.; Grainger, L. S.; Miao, K.; Fares, M.; Hoelzel, C. A.; Yennawar, H. P.; Ning, G.; Du, M.; Bai, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.* “Modulation of fluorescent protein chromophores to detect protein aggregation with turn-on fluorescence”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 24: 7381-7384.

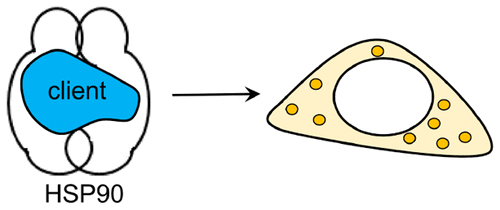
42. Pedley, A. M.; Karras, G. I.; Zhang, X.; Lindquist, S.; Benkovic, S. J.* “Role of HSP90 in the regulation of de novo purine biosynthesis”, Biochemistry 2018, 57, 23: 3217-3221.
41. Li, X.; Wang, T.; Duan, P.; Baldini, M.; Huang, H. -T.; Chen, B.; Juhl, S. J.; Koeplinger, D.; Crespi, V. H.; Schmidt-Rohr, K.; Hoffmann, R.; Alem, N.; Guthrie, M.; Zhang, X.; Badding, J. V.* “Carbon nitride nanothread crystals derived from pyridine”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 15: 4969-4972.

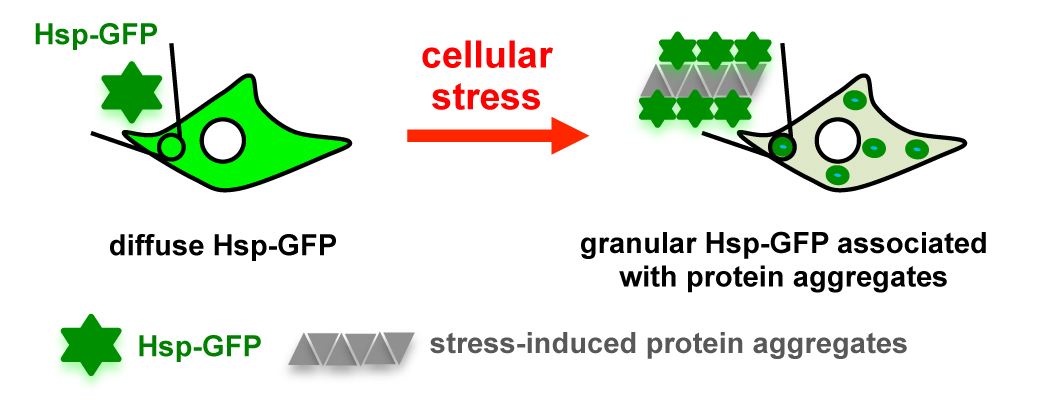
40. Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.* “Heat shock protein reports on proteome stress”, Biotechnol. J. 2018, 13, 4: 1800039.
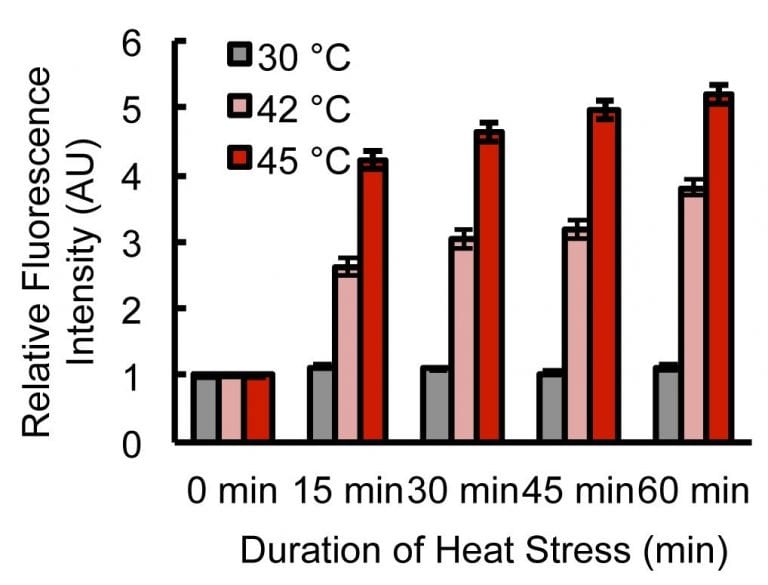
39. Fares, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Miao, K.; Gao, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, X.* “A molecular rotor-based Halo-tag ligand enables a fluorogenic proteome stress sensor to detect protein misfolding in mildly stressed proteome”, Bioconjugate Chem. 2018, 29, 1: 215-224.
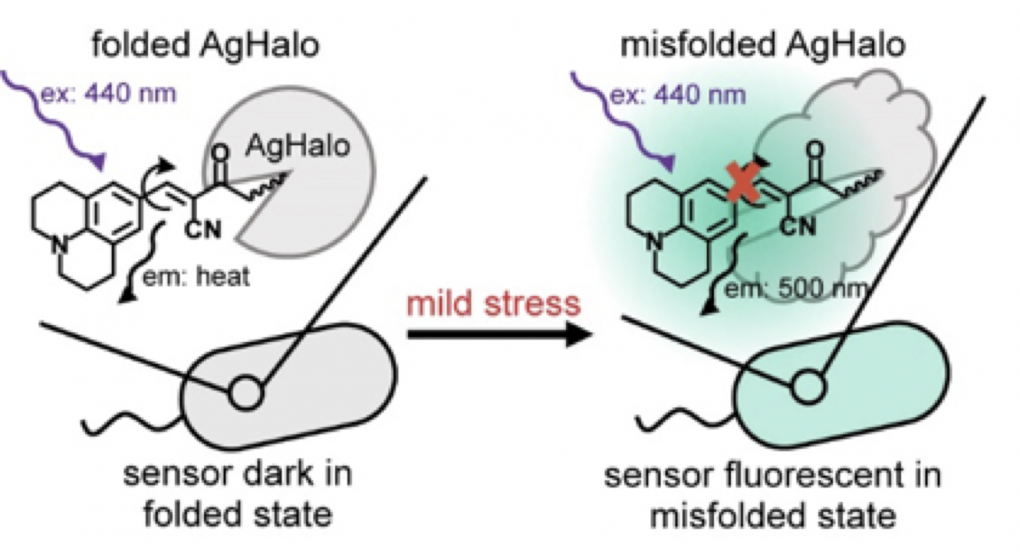
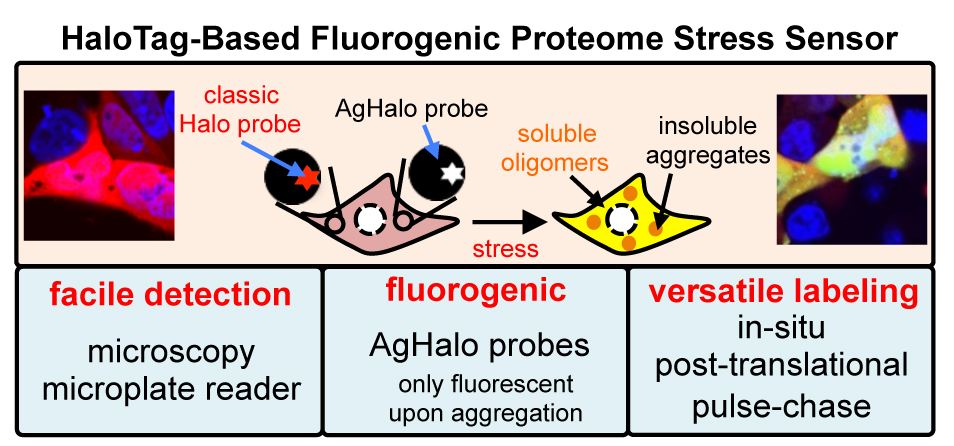
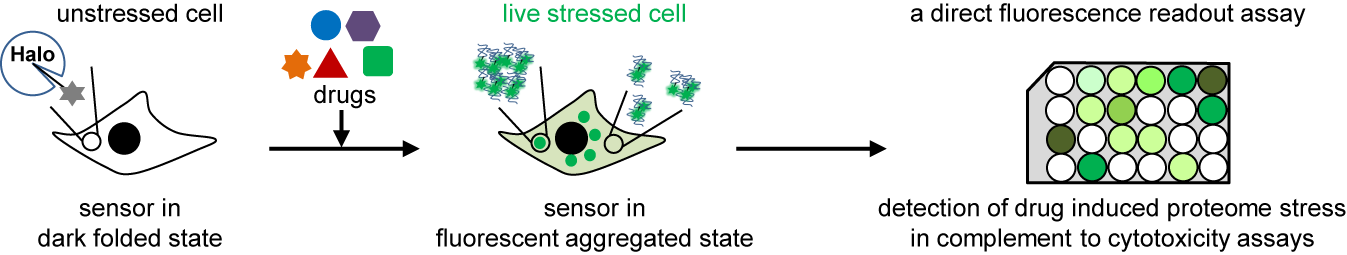
38. Liu, Y.; Fares, M.; Dunham, N. P.; Gao, Z.; Miao, K.; Jiang, X.; Bollinger, S. S.; Boal, A. K.; Zhang, X.* “AgHalo: A facile fluorogenic sensor to detect drug-induced proteome stress”, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 30: 8672-8676.
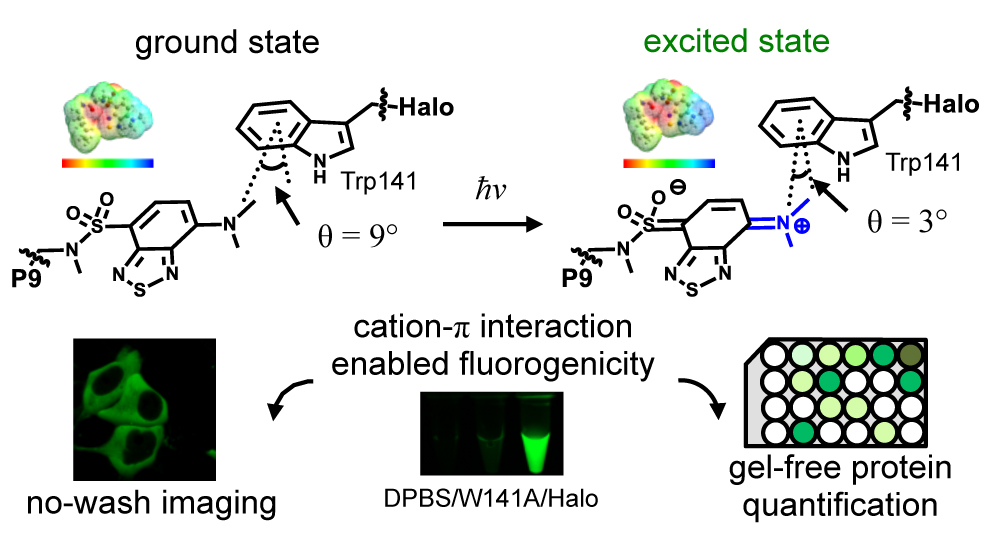
37. Liu, Y.; Miao, K.; Dunham, N. P.; Liu, H.; Fares, M.; Boal, A. K.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.* “The cation-π interaction enables a Halo-Tag fluorogenic probe for fast no-wash live cell imaging and gel-free protein quantification”, Biochemistry 2017, 56, 11: 1585-1595, (ACS Editor’s Choice). Featured by Viewpoint in Biochemistry.
From Scripps and Caltech:
36. Liu, Y.;# Zhang, X.;# Chen, W.; Tan, Y. L.; Kelly, J. W.* “Fluorescence turn-on folding sensor to monitor proteome stress in live cells”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 35: 11303-11311, (co-first authors).

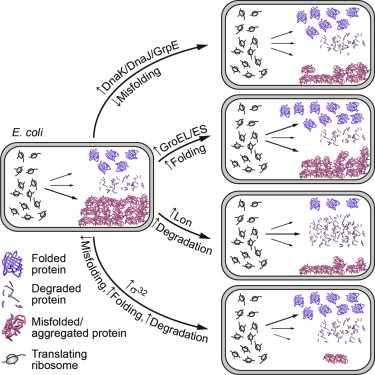
35. Cho, Y.; Zhang, X.; Pobre, K. F. R.; Liu, Y.; Powers, D. L.; Kelly, J. W.; Gierasch, L. M.;* Powers, E. T.* “Individual and collective contributions of chaperonin and degradation to protein homeostasis in E. coli”, Cell Reports, 2015, 11, 2: 321-333.
34. Liu, Y.;# Tan, Y. L.;# Zhang, X.;# Bhabha, G.; Ekiert, D. C.; Genereux, J. C.; Cho, Y.; Kipnis, Y.; Bjelic, S.; Baker, D.; Kelly, J. W.* “Small molecule probes to quantify the functional fraction of a specific protein in a cell with minimal folding equilibrium shifts”, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 2014, 111, 12: 4449-54.
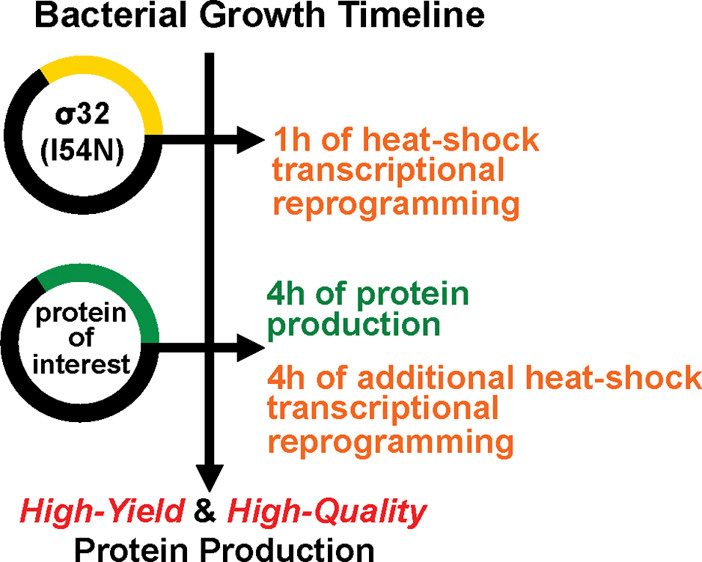
33. Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Genereux, J. C.; Nolan, C.; Singh, M.; Kelly, J. W.* “Heat-shock response transcriptional program enables high-yield and high-quality recombinant protein production in Escherichia coli”, ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9: 1945−1949. (ACS Editor’s Choice)
32. Liu, Y.;# Zhang, X.;# Tan, Y. L.; Bhabha, G.; Ekiert, D. C.; Kipnis, Y.; Bjelic, S.; Baker, D.; Kelly, J. W.* “De novo-designed enzymes as small-molecule-regulated fluorescence imaging tags and fluorescent reporters”, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 38: 13102-13105 (co-first authors).

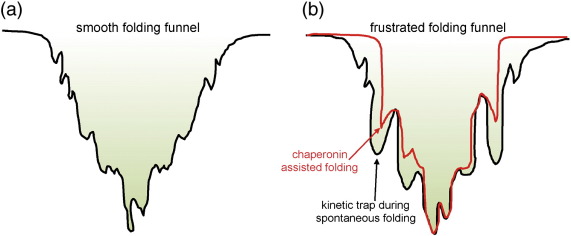
31. Zhang, X.; Kelly, J. W.* “Chaperonins resculpt folding free energy landscapes to avoid kinetic traps and accelerate protein folding” J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 15: 2736-2738.
30. Zhang, X.; Shan, S.* “Fidelity of cotranslational protein targeting by the signal recognition particle”, Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2014, 43: 381-408.
29. Akopian, D.;# Shen, K.;# Zhang, X.;# Shan, S.* “Signal recognition particle: An essential protein-targeting machine”, Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82: 693-722 (co-first authors listed alphabetically).

28. Li, X.;* Zhang, X.; Ladiwala, A. R. A.; Du, D.; Yadav, J. K.; Tessier, P. M.; Wright, P. E.; Kelly, J. W.; Buxbaum, J. N.* “Mechanism of transthyretin inhibition of β-amyloid aggregation in vitro”, J. Neuroscience 2013, 33, 50: 19423-19433.
27. Loeffelholz, O. v.; Knoops, K.; Ariosa, A.; Zhang, X.; Karuppasamy, M.; Huard, K.; Schoehn, G.; Berger, I.; Shan, S.;* Schaffitzel, C.* “Structural basis of signal sequence surveillance and selection by the SRP-FtsY complex”, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20: 604-610.
26. Liu, X.;# Wei, W.;# Yuan, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, N.; Du, Y.; Ma, G.; Yan, C.; Ma, D.* “Apoferritin–CeO2 nano-truffle that has excellent artificial redox enzyme activity”, Chem. Comm. 2012, 48: 3155-3157.
25. Zhang, X.; Lam, V. Q.; Mou, Y.; Kimura, T.; Chung, J.; Chandrasekar, S.; Winkler, J. R.; Mayo, S. L.; Shan, S.* “Direct visualization reveals dynamics of a transient intermediate during protein assembly”, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 2011, 108, 16: 6450-55.
24. Shen, K.; Zhang, X.; Shan, S.* “Synergistic actions between the SRP RNA and translating ribosome allow efficient delivery of the correct cargos during cotranslational protein targeting”, RNA 2011, 17, 5: 892-902.
23. Yang, M. -J.; Zhang, X.* “Molecular dynamics simulations reveal structural coordination of Ffh-FtsY heterodimer towards GTPase activation”, Proteins 2011, 79, 6: 1774-1785.
22. Yang, M. -J.; Pang, X. -Q.; Zhang, X.; Han, K. -L.* “Molecular dynamics simulation reveals preorganization of the Chloroplast FtsY towards complex formation induced by GTP binding”, J. Struct. Biol. 2011, 173, 1: 57-66.
21. Zhang, X.; Rashid, R.; Wang, K.; Shan, S.* “Sequential checkpoints govern substrate selection during cotranslational protein targeting”, Science 2010, 328, 5979: 757-60.
20. Yang, M.; Zhang, X.; Han, K.* “Molecular dynamics simulation of SRP GTPases: towards an understanding of complex formation from equilibrium fluctuations”, Proteins 2010, 78, 10: 2222-2237.
19. Zhang, X.; Schaffitzel, C.; Ban, N.; Shan, S.* “Multiple conformational switches in a GTPase complex control co-translational protein targeting”, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. (USA) 2009, 106, 6: 1754-59.
18. Schmid, S. L.; Zhang, X.; Shan, S.* “Signal recognition particle (SRP) and SRP receptor: A new paradigm for multi-state regulatory GTPases”, Biochemistry 2009, 48, 29: 6696–6704.
17. Wu, E. L.; Wong, K. Y.; Zhang, X.; Han, K.;* Gao, J.* “Determination of the structure form of the fourth ligand of zinc in acutolysin a using combined quantum mechanical and molecular mechanical simulation”, J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 8: 2477–2485.
16. Zhang, X.; Kung, S.; Shan, S.* “Demonstration of a multistep mechanism for assembly of the SRP•SRP receptor complex: Implications for the catalytic role of SRP RNA”, J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 381, 3: 581-593.
15. Zhang, X.; Han, K. -L.* “High-order symplectic integration in quasi-classical trajectory simulation: Case study for O(1D)+H2”, Int. J. Quantum. Chem. 2006, 106, 8: 1815-1819.
14. Chu, T.; Zhang, X.; Ju, L.; Yao, L.; Han, K. -L.;* Wang, M.; Zhang, J. Z. H.* “First principles quantum dynamics study reveals subtle resonance in polyatomic reaction: The case of F+CH4 → HF+CH3”, Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 424, 4-6: 243-246.
13. Chen, X.; Zhang, X.; Han, K.;* Varandas, A. J. C.* “Ab initio study of the H+ClONO2 reaction”, Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 421, 4-6: 453-59.
12. Ju, L. -P.; Xie, T. -X.; Zhang, X.; Han, K. -L.* “A modified potential energy surface for the C2H+H2↔ C2H2+H reaction and a theoretical study on its rate constants”, Chem. Phys. Lett. 2005, 409, 4-6: 249-254.
11. Chu, T.; Zhang, X.; Han, K. -L.* “A quantum wave-packet study of intersystem crossing effects in the O(3P, 1D)+H2 reaction”, J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 122, 21: 214301-214306.
10. Yang, G.; Yao, L.; Zhang, X.; Meng, Q.; Han, K. -L.* “Theoretical study of the mechanism for spin-forbidden quenching process O(1D)+CO2 (1Sg+) → O(3P)+CO2 (1Sg+)”, Int. J. Quantum. Chem. 2005, 105, 2: 154-159.
9. Yang, C. -L.;* Zhang, X.; Han, K. -L. “Theoretical study on analytical potential function and spectroscopic parameters for CaF molecule”, J. Mol. Struct-Theochem 2004, 678, 1-3: 183-188.
8. Yang, C. -L.;* Zhang, X.; Han, K. -L. “Ab initio geometries, electronic structures of MgB2 molecule”, J. Mol. Struct-Theochem 2004, 677, 1-3: 11-14.
7. Yang, C. -L.;* Zhang, X.; Han, K. -L. “Analytical potential energy function and spectroscopic parameters for the ground and excited states of NaH”, J. Mol. Struct-Theochem 2004, 676, 1-3: 209-213.
6. Yang, G.;* Zhang, X.; Meng, Q.; Han, K. “Theoretical studies on the intermediate complex mechanism of the energy transfer reaction of O(1D)+CO2 (1Sg+) → O(3P)+CO2 (1Sg+)”, Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2004, 25, 4: 689-692.
5. Yang, G.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Han, K.* “Theoretical study on the formation mechanism of iso-CH2l-Cl”, Int. J. Quantum. Chem. 2004, 97, 2: 719-724.
4. Zhang, X.; Yang, G. -H.; Han, K. -L.;* Wang, M. -L.; Zhang, J. Z. H. “Quantum dynamics study of isotope effect for H + CH4 reaction using the SVRT model”, J. Chem. Phys. 2003, 118, 20: 9266-9271.
3. Yang, C. -L.;* Huang, Y. -J.; Zhang, X.; Han, K. -L. “MRCI potential curve and analytical potential energy function of the ground state of H2”, J. Mol. Struct-Theochem 2003, 625, 1-3: 289-293.
2. Zhang, X.; Han, K.;* Zhang, J. Z. H. “SVRT calculation for bond-selective reaction H+HOD → H2+OD, HD+OH”, J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 116, 23: 10197-10200.
1. Zhang, X.; Xie, T.; Zhao, M.; Han, K.* “Quasiclassical trajectory simulation of the chemical reaction Ba+HF (n, J) → BaF (n‘, J‘)+H”, Chin. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 15, 3: 169-174.
